3 Nov 2025
Digital Cognitive Twins: The Hidden Face of the Data War
Simulation technology is witnessing a profound transformation with the emergence of Digital Cognitive Twins (DCTs), the next generation of Traditional Digital Twins (DTs). These advanced systems go beyond conventional monitoring functions, integrating sophisticated AI models, particularly machine learning networks and natural language processing (NLP) techniques.
This convergence grants DCTs complex capabilities, enabling them to perform autonomous decision-making, conduct real-time self-optimisation, and develop predictive and anticipatory mechanisms. As a result, this technology is reshaping key sectors across multiple domains. In Industry 4.0, it enhances the efficiency and resilience of logistical supply chains; in urban governance, it enables the intelligent management of resources with exceptional accuracy; and in the healthcare sector, it accelerates the adoption of precision medicine tailored to the individual.
The exceptional performance of these systems depends on their ability to absorb and aggregate vast datasets, comprising thousands of variables for a single individual. These datasets extend well beyond the conventional boundaries of personal information, encompassing biometric inputs, genomic data, clinical records, and continuous monitoring of behavioural and psychological patterns derived from digital interactions.
This aggregation produces human simulation models of exceptional fidelity, a defining feature that places this technology squarely within the dual-use domain. While these models promise vast societal benefits, the compromise or seizure of these composite data repositories would constitute a catastrophic national security threat: the harm arising from the exposure of citizens’ data would be strategic, permanent, and irreparable.
The gravest risk lies in the possibility that state or non-state actors might exploit these datasets. Whereas past influence operations—most notably the disinformation campaigns of the last decade—targeted broad audiences, behavioural models derived from integrated digital-transformation processes enable bespoke cognitive-warfare interventions at the level of individuals or small groups. This capability transcends conventional geopolitical forecasting, enabling real-time prediction of societal behaviour.
At the core of the threat is the capacity to selectively manipulate these datasets or even fabricate synthetic records to engineer a pretext for intervention. By corrupting cognitive models, an adversary can simulate a manufactured state of public unrest, precipitate mass psychological collapse, or stage apparent systemic institutional failure—thereby manufacturing a spurious justification for political, economic or security interventions.
20 Oct 2025
The Future Role of China in the GCC’s Tech Transition
China has a long-term goal to be a global leader in technology. To achieve such ambition, the country has taken serious steps widening its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) traditional infrastructure projects to incorporate digital infrastructure projects embodied in the Digital Silk Road (DSR). The DSR was initially launched in 2015 by the government as an idea on paper and during the opening ceremony of the First Belt and Road Forum in May 2017, China’s President Xi Jinping, adopted the DSR term officially and it was incorporated in the government’s BRI strategy as the digital dimension.
The DSR initiative focuses on building digital infrastructure and exporting its technology to the beneficiary countries, it includes telecommunications infrastructure, like 5G networks, overland fibre-optic cables, data centres, cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), as well as applications that support e-commerce and mobile payments, along with smart cities and surveillance technology. Additionally, the DSR provides support to Chinese tech companies, like ZTE, Huawei, and Alibaba, to carry on the work with the beneficiaries.
The DSR aims to enhance Beijing's global digital influence as it creates opportunities for a wide range of cooperation and partnerships between Chinses tech companies and other beneficiaries around the world in areas of digitalization and AI. China’s DSR encompass a variety of projects in 5G deployment, e-commerce platforms, and AI applications, such as DeepSeek which is an alternative model to ChatGPT.
China signed DSR cooperation agreements with several countries in Africa, the Middle East, Eastern Europe, Latin America, and Southeast Asia. The cooperation takes place between scientists and engineers from the recipient country and Beijing, like opening a training centre or in research and development (R&D). The areas of cooperation are wide, including smart cities, AI and robotics, clean energy, and surveillance capabilities, like data localization. GCC countries are considered one of the important partners to China’s DSR, where it is closely integrating in the GCC digitalization goals.
16 Oct 2025
Algorithms of Genocide: From Silicon Valley to the Gaza Strip
The tools of twenty-first-century warfare are no longer confined to conventional weapons such as missiles, tanks, and aircraft. They have expanded to encompass cloud-computing platforms, artificial-intelligence systems, and data-processing capabilities developed and managed by major U.S.-based technology corporations, including Microsoft, Google, and Amazon. These companies have become central pillars in the conduct of modern digital warfare, with their decisions and policies exerting profound geopolitical influence and forming an integral component of contemporary global power dynamics.
In this context, the relationship between commercial technology corporations and the Israeli military has undergone a profound transformation, moving beyond the traditional model of supplying hardware and software to establish digital infrastructure as a central instrument in the management of modern conflict, most notably during the war on Gaza. A new paradigm of integration between the military and the private sector has emerged, in which commercial digital systems have become an inseparable component of military capability, blurring the boundaries between market-driven services and state security architectures.
The management of the global narrative surrounding humanitarian catastrophes, including the confirmed famine and persistent reports of atrocities, has become inseparable from the content-governance policies imposed by major digital platforms controlled by technology conglomerates. These platforms frequently amplify official narratives while minimising or obscuring the magnitude of famine and conflict. At the same time, they enable advanced surveillance mechanisms that restrict or silence independent media operating within conflict zones.
The war in Gaza has underscored the dual and increasingly intricate role of major technology corporations, particularly Google (Alphabet Inc.) and Microsoft Corporation, in both modern warfare and global information control. These entities operate within a mutually reinforcing dynamic, providing specialised cloud-computing and artificial-intelligence infrastructure that enables unprecedented levels of lethal military operations and mass surveillance across Gaza and the occupied territories. Concurrently, they deploy advanced mechanisms of information control, encompassing internal content moderation, algorithmic bias, and data suppression, to recalibrate public narratives and shield corporate power from accountability.
This analysis, therefore, examines the role of technology corporations in shaping the dynamics and repercussions of the conflict in Gaza, exploring how they contribute to the engineering of the informational, political, and humanitarian landscape within the framework of contemporary warfare. In this process, these corporations are transformed from ostensibly neutral service providers into active participants within the conflict’s infrastructural ecosystem.
14 Oct 2025
What Would Iran’s Withdrawal from the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty Mean?
Iran’s nuclear file is witnessing a rapidly escalating trajectory, underscored by its potential decision to withdraw from the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT). This move could redefine the very architecture of global nuclear governance. Should this course of action materialise, it would mark the first precedent of its kind since North Korea’s withdrawal from the same treaty in 2003, transforming what might initially appear as a mere negotiating stance into a profound strategic turning point with far-reaching implications for the policies of the Middle East and the wider international order.
These Iranian threats, which began escalating in June 2025, did not emerge in a vacuum; instead, they were a direct reaction to a series of successive strategic developments. The U.S.–Israeli military strikes targeting Iranian nuclear facilities in June 2025 significantly deepened the complexity of the situation, while the crisis further intensified when the European troika (E3) announced in September 2025 the activation of the “snapback mechanism,” thereby reimposing UN sanctions on Tehran. Taken together, these measures led Iran to conclude that the economic and political value of adhering to international treaties had effectively evaporated.
The gravity of the situation extends beyond political dimensions to encompass highly sensitive technical and legal aspects. Technically, Iran possesses between 400 and 450 kilograms of uranium enriched to roughly 60%; a stockpile that places it only weeks away from producing weapons-usable fissile material if enrichment were elevated to about 90%. Legally, Iran’s invocation of Article X of the NPT would trigger an immediate cessation of the International Atomic Energy Agency’s (IAEA) oversight and remove the Comprehensive Safeguards Agreement from the equation, paving the way for near-total diplomatic isolation. Consequently, the fallout from withdrawal would transcend the confines of Tehran’s nuclear programme and create a broad regional security dilemma.
9 Oct 2025
US Intelligence Support Signals a New Phase in the Russia-Ukraine War
On October 1, U.S. reports stated that President Donald Trump gave the green light to provide Ukraine with intelligence information to strike deep into Russia’s energy infrastructure sites, while studying providing Kyiv with long-range weapons that can be used in such strikes. The reports also indicated that Washington is encouraging the NATO allies to take similar actions.
The U.S. has already been providing intelligence to Ukraine since the beginning of the war; however, Trump's signalling to provide more sensitive information could hold different consequences on the outcomes of the war. Since his second-term inauguration, Trump has vowed to end the Russia-Ukraine war, so does this decision come in parallel to the American President's ambition to broker a peace deal between Moscow and Kyiv, and how this might implicate the Russian and Ukrainian sides.
2 Oct 2025
Nation on Edge: Intensified Political Polarisation in the U.S.
The shooting of the right-wing conservative activist Charlie Kirk on September 10 at Utah Valley University in Orem, Utah, during a question-and-answer debate, reflects the deep divisions in American society and the political landscape and represents a repercussion of the polarised America and increased political violence.
Where Ideological polarisation in the U.S. has been deeply rooted in society, and recent times have witnessed a more divided landscape over the governmental domestic and foreign policy directions, including taxes, immigration, aid to Ukraine, and Israel's war in Gaza. Since the outbreak of the Gaza war, the U.S. government has been providing extensive military, financial, and diplomatic support for Israel. Additionally, the U.S. repeatedly vetoed several UN ceasefire resolutions, widening the gap between the government's direction and the street, especially among younger generations. The American campuses witnessed a wide range of protests against Israel's war in Gaza and in support of Palestine, which were met by violence from the police forces, arrests, and threats of deportation for foreign students. Similarly, Kirk has been a strong supporter of Israel and its actions in Gaza but raised doubts on Israel’s security breaches and how Hamas was able to penetrate Israel's defence system.
Kirk was a symptom of the polarisation in the U.S. His opinions rallied many people around him and often clashed with the Democrats’ views, raising questions about the possibility that his shooting was a manifestation of deep polarisation inside American society and whether divisions over issues such as gender, immigration, and the Gaza war are key incentives for the ongoing polarisation-induced violence in the U.S.
With the mayoral and midterm congressional elections approaching, questions are raised about whether the Republican Party will utilise the political violence fuelled by intense polarisation to secure electoral gains and whether the Democratic Party can overcome internal divisions and capitalise on the concerns about the Trump administration’s heavy-handed response to Kirk’s assassination.
18 Sep 2025
The Semiconductor Cold War: U.S. vs. Russia, China and India
The global competition over semiconductors and related military technologies has become the central axis of great-power rivalry. The United States maintains its leadership in the global semiconductor industry, with American companies securing roughly half of the global semiconductor market. However, this dominance faces a growing challenge from China, which accounted for 20% of global semiconductor sales in 2024. Beijing’s ambition to achieve self-sufficiency in semiconductors is steadily advancing despite ongoing trade tensions and intellectual property restrictions imposed by Washington amidst the broader ‘tech war.’ China aims to reach 50% self-sufficiency in semiconductor production by the end of the year, reinforced by significant investments in R&D and market expansion by Chinese firms.
In contrast, Russia’s position in semiconductor-dependent military industries is increasingly constrained. Although Russia retains expertise in weapons design, its reliance on imported materials and advanced chip-making equipment from Western countries exposes critical vulnerabilities. Western sanctions, introduced in response to Russia’s military actions in Ukraine, have sharply limited Moscow’s access to these essential inputs. In response, Russia has sought alternative suppliers, with China emerging as its largest source of semiconductor materials. These dynamic forms part of the broader Russia-India-China (RIC) trilateral framework, underpinning Moscow’s strategic pivot toward Eastern partnerships.
Meanwhile, India is rapidly evolving as a significant player in the semiconductor sector. The country’s announcement in September of its first indigenous chip, “Vikram 32,” marks a milestone in New Delhi’s pursuit of technological self-reliance and signals India’s potential emergence as a competitor to U.S. semiconductor dominance. India’s increasing engagement with Russia and China reflects a pragmatic alignment based on mutual interests, particularly in the context of escalating policy tensions with Washington. Notably, U.S. tariffs imposed on India’s trade in Russian oil have further incentivized this trilateral collaboration.
Collectively, the China-Russia-India “troika” represents a coalition of shared interests rather than a formal ideological alliance. Should this partnership strengthen, it could significantly bolster their semiconductor manufacturing capabilities and pose a formidable challenge to the American industry. Nevertheless, lingering frictions—such as unresolved border disputes, differing economic priorities, technological gaps, and the impact of sanctions—are likely to impede seamless technological integration. The United States still wields substantial influence over India, with opportunities to attract New Delhi through increased investments, tariff reductions, and advanced technology cooperation. Ultimately, the trajectory of the RIC semiconductor partnership holds profound implications for the global order. A successful integration of this “troika” chip industry with their respective military technologies could catalyse the rise of a multipolar system, revolutionizing surveillance, air defence, drone capabilities, and the broader defence industrial base, thereby reshaping international power dynamics.
16 Sep 2025
The Arab-Islamic Emergency Summit: A Watershed Moment in Regional Dynamics
The 2025 Arab–Islamic extraordinary summit, held in Doha, Qatar, on September 14–15, marked a pivotal moment in Middle Eastern diplomacy. Convened in direct response to an unprecedented Israeli airstrike on the Qatari capital, the meeting served as a forum for Arab and Islamic nations to formalise a collective security and diplomatic response. The paper finds that this Israeli action, intended to undermine ongoing negotiations, inadvertently solidified a unified front among regional powers. The incident also exposed a profound erosion of trust in the United States as a reliable security partner, compelling Gulf states to actively consider alternative defence and diplomatic alignments. The summit's outcomes signal a new phase of regional foreign policy, moving beyond rhetorical condemnation to a framework for coordinated legal and economic measures, with significant implications for Israel, the United States, and the prospects for a lasting ceasefire in Gaza.
The final communiqué went far beyond rhetoric, demanding concrete punitive and legal measures against Israel. These included a call for sanctions, a review of diplomatic relations, and the use of international legal bodies to hold Israel accountable. The activation of the Gulf Cooperation Council’s (GCC) Joint Defence Council signalled a tangible move toward a new, collective regional security paradigm. The summit’s outcomes collectively demonstrate a strategic pivot away from American-led diplomacy and security frameworks toward a more independent and potentially confrontational regional posture, signalling a new, more volatile era in Middle East geopolitics.
15 Sep 2025
Trump Peace Play: Three Futures for Russia-Ukraine War
Amid Trump’s meetings with Russian & Ukrainian counterparts to reach a prolonged ceasefire, questions arise about the possibility of a successful peace plan occurring between Moscow & Kyiv with a U.S. mediation. Yet, with Putin’s demands from one side and Trump’s ambiguous promises to Zelensky from the other side, will the Ukraine war come to an end?
17 Aug 2025
Domino Effect: Are More States Moving Toward Recognising Palestine?
Recent statements by France, the United Kingdom, and Canada—subsequently echoed by other European states—on their intention to recognise a Palestinian state in September mark a notable transformation in the policies of major Western powers toward the Palestinian question. This development comes against the backdrop of the deepening humanitarian catastrophe in Gaza, manifested in widespread famine and a death toll exceeding 60,000, which has further amplified international calls for an urgent political resolution to the decades-long Israeli–Palestinian conflict.
The announcements from Paris, London, and Ottawa—particularly France’s unconditional pledge alongside the conditional approaches adopted by the United Kingdom (UK) and Canada—represent a clear departure from traditional diplomatic norms, which had long tied recognition of a Palestinian state to the conclusion of a comprehensive negotiated peace agreement. This shift reflects mounting frustration over the stalled peace process, coupled with a growing conviction that conventional pathways have ceased to yield results. Recognition of Palestine is now increasingly seen not merely as the outcome of peace but as an instrument to catalyse the political process, thereby reshaping the diplomatic tools available for addressing the conflict and establishing a precedent that other states may exploit to strengthen international pressure.
At the international level, between 140 and 147 of the 193 UN member states already recognise Palestine as a sovereign state. This broad consensus provides the reference framework for understanding the recent decisions taken by France, the UK, and Canada. Notably, these three countries are all members of the G7, none of which had taken such a step before France’s declaration. France—Europe’s most populous nation—thus emerges as a prominent actor in this diplomatic shift, with both France and Canada poised to become the first G7 states to extend formal recognition to Palestine.
By contrast, the U.S. remains the sole permanent member of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) that has yet to recognise the State of Palestine. This imbues the current shift with symbolic weight, laying the groundwork for a recalibration of diplomatic pressure on both Israel and the U.S., and potentially encouraging other hesitant Western states to follow suit. The divergence of positions within the Atlantic powers also underscores how internal pressures and the urgency of the humanitarian crisis have shaped the emergence of more assertive stances. Against this backdrop, this analysis explores the drivers behind this shift and its political and security implications for the states concerned, alongside the anticipated responses from Israel and the U.S.
17 Aug 2025
Larijani’s Visit: Building Alliances or Rescuing Allies?
Iran’s militias in Iraq and Lebanon are currently grappling with multi-dimensional crises, including the erosion of their political influence, mounting military pressures, and the need to recalibrate their strategies amid shifting regional alliances in a volatile regional and international environment. These challenges are undermining their ability to sustain the role they once played within Iran’s “Axis of Resistance.” This situation coincides with the visit of the Secretary of Iran’s Supreme National Security Council, Ali Larijani, at a particularly critical and sensitive moment. The visit represents either an opportunity to forge new alliances or an attempt to rescue embattled allies in Iraq and Lebanon.
23 Jul 2025
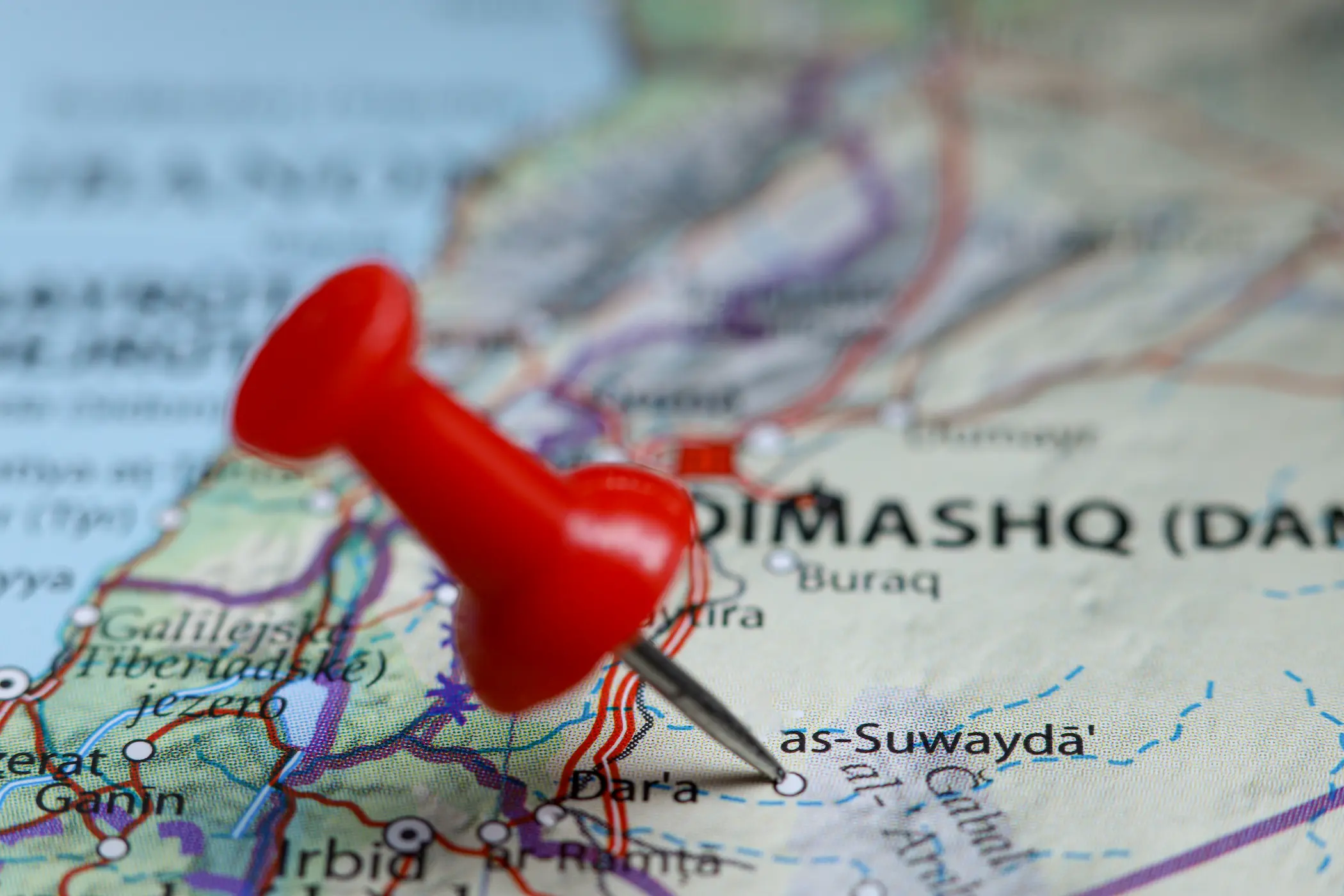
Could As-Suwayda Reshape the Calculations of the Syrian Democratic Forces?
With the fall of Bashar al-Assad's regime in December 2024, Syria entered a pivotal political turning point, ushering the country into a new phase. Ahmad al-Sharaa assumed the role of interim president, and this transitional period has been defined by intense efforts to restore security and stability, unify the divided armed factions, and address the growing humanitarian needs nationwide. Against this shifting backdrop, the southern governorate of As-Suwayda, home to a Druze majority, emerged as a strategic hot spot of tension. Recent military developments in the region have taken on significant dimensions, potentially impacting the future of the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) in the country's northeast.