Mostafa’s research and writings focus on regional and international security, while his contributions deal primarily with gulf security, conflict resolution, and negotiations. His research has supported decision-makers in across multiple governmental bodies.
Prior to joining Al Habtoor Research Centre, Mostafa was a lecturer of International Relations at Mongolia International University. He obtained his first master’s degree in International Relations from Porto University, and obtained his second master’s degree from Korea Development Institute (KDI), one of the leading think tanks in Asia.
contact information
Latest By Mostafa Ahmed
23 Jun 2025
Containment to Confrontation: US Intervention in Iran
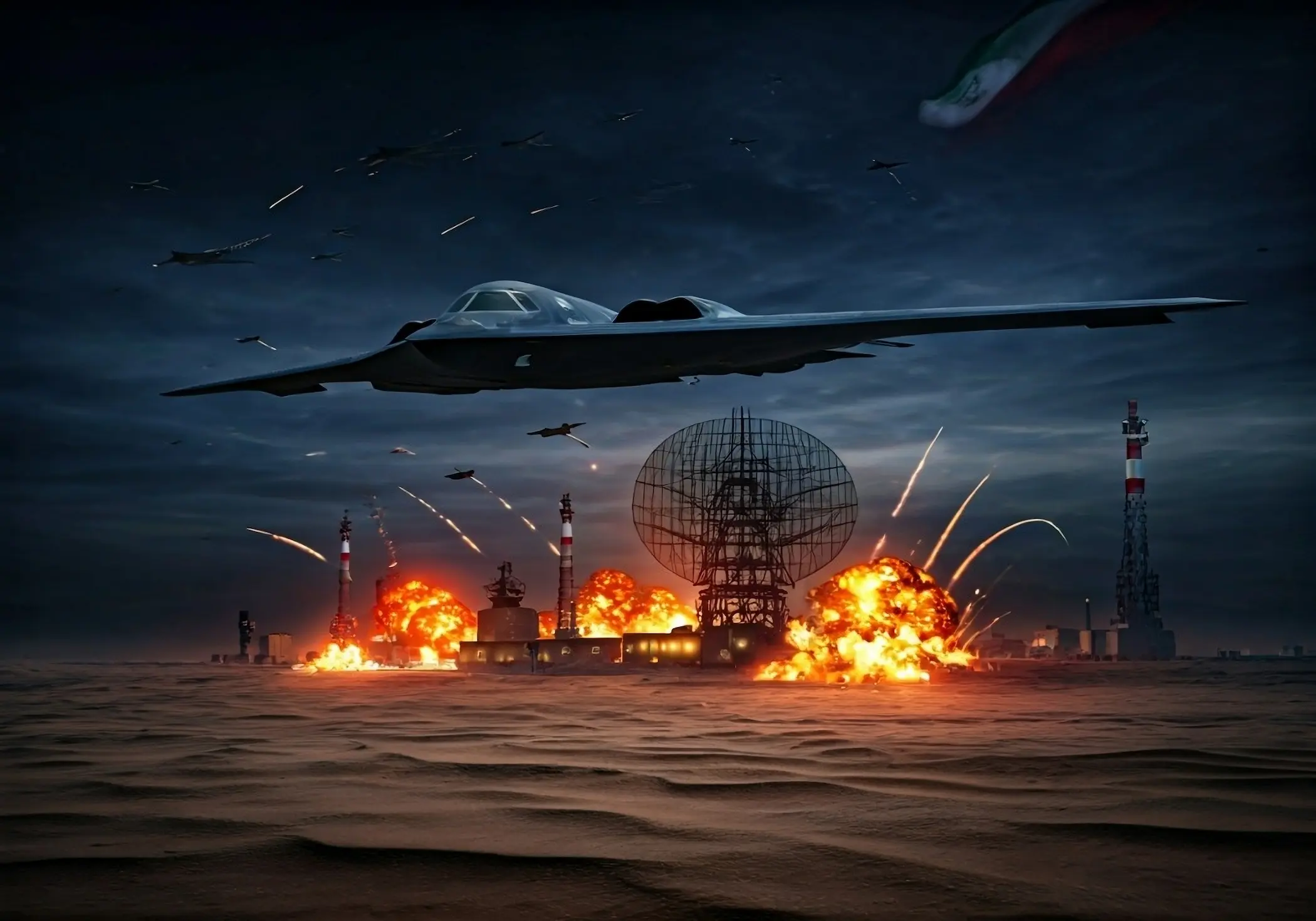
In the early hours of June 22, 2025, the Middle East entered a new phase of strategic confrontation following the United States' execution of a calibrated series of precision airstrikes against three of Iran’s most critical nuclear facilities: the Fordow Fuel Enrichment Plant, the Natanz Enrichment Complex, and the Isfahan Nuclear Technology Center. These strikes marked a significant inflection point in American policy toward Iran's nuclear program, signifying a deliberate departure from the long-preferred instruments of sanctions, diplomacy, and covert sabotage toward direct military action aimed at functionally dismantling Iran’s enrichment capacity.
The U.S. intervention did not occur in a vacuum but was preceded by a sweeping nine-day Israeli air campaign— “Operation Rising Lion”—which inflicted substantial damage on Iran’s conventional military and nuclear infrastructure. Yet U.S. strategic assessments concluded that Israeli capabilities alone would fall short of neutralizing the deeply buried Fordow facility, located nearly 90 meters beneath the mountains near Qom. Accordingly, Washington deployed B-2 Spirit bombers from Whiteman Air Force Base and launched submarine-based Tomahawk cruise missiles, employing—for the first time in combat—the GBU-57 Massive Ordnance Penetrator, a 30,000-pound precision-guided “bunker buster” weapon. The strikes were designed not merely to degrade but to decapitate Iran’s uranium enrichment trajectory at every critical juncture.
While the U.S. administration proclaimed the operation a “complete and total success,” Iran’s leadership sought to downplay the extent of the damage, signalling both resilience and continued intent to pursue its nuclear ambitions. Tehran’s initial response refrained from large-scale direct retaliation, instead signalling a likely pivot toward asymmetric reprisal via regional proxies such as the Houthis, alongside diplomatic escalation and renewed threats to abandon the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT). This calibrated restraint highlights the regime’s acute awareness of the potentially existential consequences of a direct confrontation with the United States.
Structurally, the strikes reflect a paradigmatic shift in U.S. non-proliferation doctrine: from risk management through deterrence and arms control to selective, high-precision coercion. The operation also underscores a changing regional deterrence architecture, in which American military intervention is no longer conditioned by alliance consensus or Gulf coordination, as several key Arab states were reportedly excluded from prior notification. This signals an American willingness to act unilaterally—or bilaterally with Israel—when core proliferation red lines are deemed to have been crossed.
22 Jun 2025
Iran and Israel: The War That Will Redraw the Middle East
The war between Iran and Israel is arguably a war of survival for the regime in Iran. Attacking Iran seemed to be a logical step for Israel after almost destroying its arms of proxies in the region. the regime, which stands on three pillars, namely, its conventional missile arsenal, its extensive network of regional proxy forces, and its nuclear program, is facing a war of attrition that might eventually end the very survival of the regime. The fall of the regime in Iran goes beyond mere regime change, rather, it is considered a state collapse.
The collapse of the Iranian state would have dire consequences for the region. However, the possibility of the regime surviving remains a significant scenario. While the fall of Iran is widely regarded as a regional catastrophe, its continued survival, particularly with Tehran asserting itself as a regional superpower, could prove even more destabilizing for Israel and its allies. Both outcomes carry profound regional and global implications, signalling a transformation in Middle Eastern geopolitics. The pressing question is not whether change is coming, but rather: what will the new Middle East look like?
19 Jun 2025
What If: Iran Closed the Strait of Hormuz?
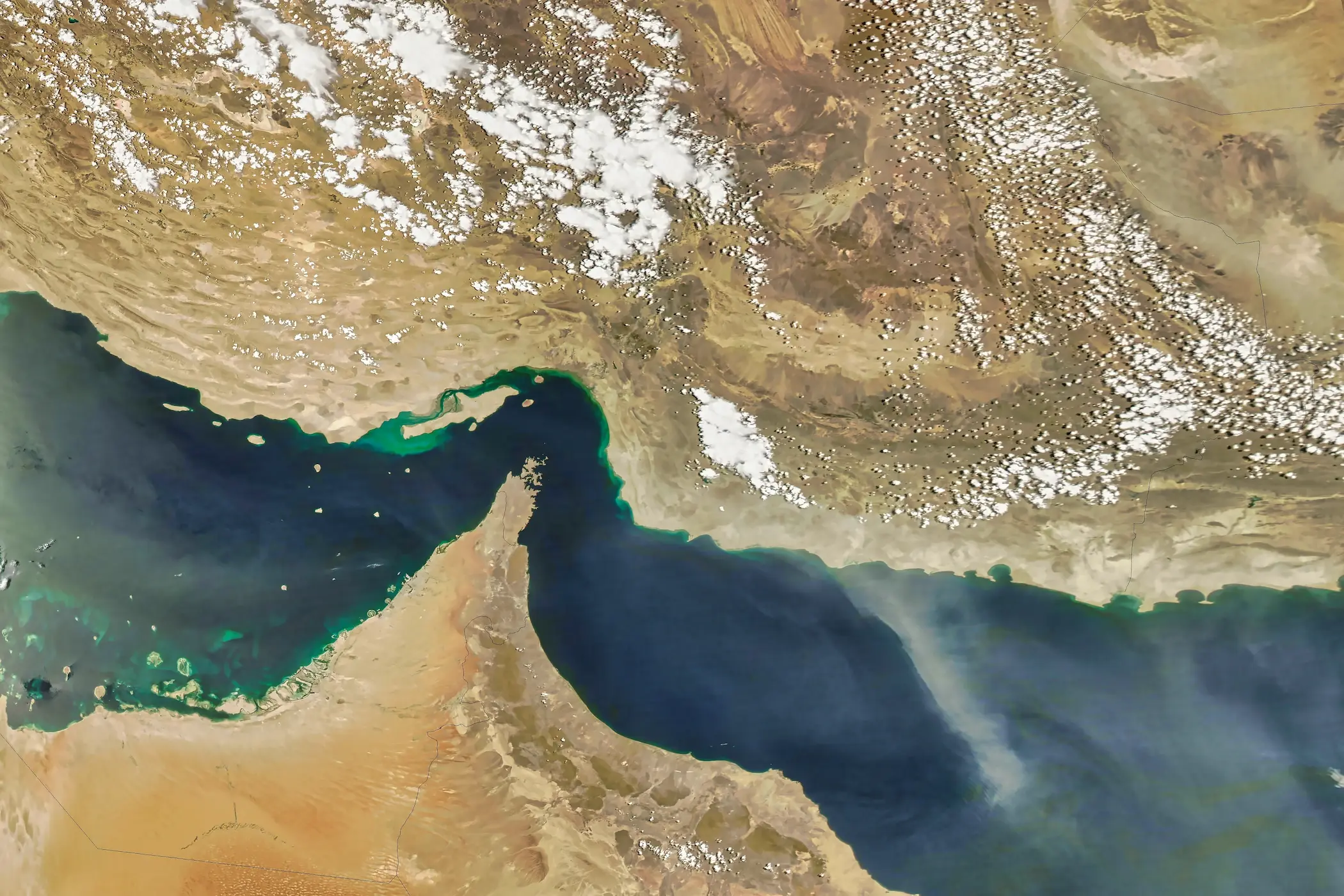
The Strait of Hormuz – a narrow, indispensable artery through which nearly a fifth of the world’s oil and a third of its liquefied natural gas (LNG) flows– stands on a cliff. As geopolitical tensions intensify across the Middle East, fuelled by escalating Iran-Israel tensions and the shadow of direct United States (U.S.) involvement, the once-unthinkable threat of its closure looms larger than ever with Iran’s threat to close or block the Strait. In spite of the catastrophic global implications of such an act, the volatile depths of this potential crisis will be explored, unravelling the motives that could push Iran to choke this global lifeline, exposing the monumental security and geopolitical fallout, and revealing the catastrophic economic shockwave that would consume nations far beyond the region.
15 Jun 2025
Why Did Iran Fail to Repel Operation Rising Lion?
Operation Rising Lion, executed by Israel on June 13, 2025, constituted a lightning strike aimed at crippling the very core of Iran's nuclear and military infrastructure. Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu characterised this pre-emptive operation as a necessary measure to "roll back the Iranian threat to Israel's very survival," drawing upon the Begin Doctrine previously brought to bear in analogous strikes against Iraq in 1981 and Syria in 2007. The operation's objectives were marked by strategic multiplicity and diversity, encompassing the targeting of numerous nuclear facilities, alongside senior Iranian military commanders and nuclear scientists, in an endeavour to inflict maximum damage upon Iran's military and nuclear capabilities. Israel's intent was not merely confined to disrupting the nuclear program; it extended to undermining Iran's capacity to mount retaliatory assaults and to fend off future waves of Israeli attacks.
The timing of the Israeli operation came on the heels of a meticulous assessment by the Israeli leadership, which had concluded that Iran was on the cusp of achieving a dangerous breakthrough in its pursuit of nuclear weaponry, thereby necessitating the exploitation of a narrow temporal window before Iranian nuclear facilities became either too advanced or too robustly protected. In this context, this analysis aims to delve into the rationale underpinning the operation, to account for Tehran's apparent failure to parry the assault effectively, and to examine the attack's repercussions on Iran's domestic landscape. Furthermore, it seeks to investigate the potential pathways Iran might pursue to reconstitute its deterrent capability.
25 May 2025
A Turning Point in Gaza: Allies’ Ultimatum May Shift the Calculus
The recent joint statement by the United Kingdom, France, and Canada, threatening "concrete actions" against Israel if it does not cease its renewed military operations in Gaza and significantly increase humanitarian aid, marks a significant shift in the international discourse surrounding the ongoing conflict.
19 May 2025
What Does the Lifting of U.S. Sanctions Mean for Syria?
The United States started putting sanctions on Syria as early as 1979, mostly because Syria was labelled as a State Sponsor of Terrorism (SST). The first designation was based on Syria's military occupation of Lebanon and its support for groups like Hezbollah that the government paid for. This early policy took a harsh and threatening stance against a government that was seen as hostile and supportive of non-state actors that were seen as a threat to U.S. interests.
After the Syrian conflict started in 2011, the U.S. greatly increased its sanctions against the Assad government. The goal of these more extensive measures was to stop the Syrian government from using violence against its people and to encourage political changes that could get to the bottom of the conflict. This was a big change from only focussing on counter-terrorism to a wider agenda that included human rights and changing the behaviour of the regime, with some elements of coercive diplomacy.
The end of Bashar al-Assad's rule in early December 2024 marks a major change in Syria's politics. This event changed the main goal of the long-standing U.S. sanctions, which were mostly aimed at the now-deposed government.
In May 2025, during a trip to Saudi Arabia, U.S. President Donald Trump made a big announcement: he would lift sanctions on Syria. He said this would "give them a chance at greatness." Many people see this announcement as a "historic development" that has "major potential to improve living conditions" and "support the Syrian political transition." The goal is to make the area more stable and improve Syria's economic prospects after years of being held back by harsh international sanctions. This paper looks at the United States' sanctions against Syria in depth, putting the recent change in policy in the context of its history and the law.
14 May 2025
What If: The India-Pakistan Ceasefire Collapses?
The recent U.S.-brokered ceasefire between India and Pakistan, following four nerve-racking days of escalating military exchanges, offered a moment of reprieve from the brink of what many feared could become an all-out conflict between the two nuclear-armed neighbors. Missiles and drones crossed borders, tensions were sky-high, and the language from both capitals was increasingly aggressive. President Trump's sudden announcement of a truce, while welcomed, underscored the inherent fragility of the situation. Amid celebrations in India and Pakistan, and self-congratulations in Washington, Kashmir endured another night of violence, with both sides claiming violations. This temporary calm exists against a backdrop of deep-seated historical grievances, unresolved territorial disputes, evolving nuclear doctrines, and a complex interplay of internal and external pressures. The critical question now is not just how the ceasefire was achieved, but whether it can hold, and what the consequences would be if this fragile truce were to collapse.
8 May 2025
Hezbollah 2.0: The Future of the Party in Lebanon
Hezbollah stands at a pivotal crossroads, navigating the turbulent aftermath of a devastating conflict with Israel and grappling with profound shifts in its domestic politics and the regional strategic map. The cessation of hostilities, marked by a U.S.-brokered ceasefire effective Nov. 27, 2024, brought an end to intense fighting that inflicted immense human suffering and infrastructural damage across the country. This fragile peace coincided with, and was significantly influenced by two seismic events: the sudden collapse of the al-Assad regime in Syria, severing Hezbollah’s critical land bridge to Iran, and the end of a paralyzing two-year presidential vacuum in Lebanon with the election of the Lebanese Armed Forces (LAF) Commander General Joseph Aoun, who has promised to dismantle Hezbollah’s military structure and restrict access to weapons, these promises were likely possible to make because of Hezbollah's significantly weakened state.
The 2024 conflict dealt an unprecedented blow to Hezbollah, resulting in the decapitation of its leadership, including longtime leader Hassan Nasrallah and his designated successor; the death of thousands of its fighters; the depletion of its arsenal; and the destruction of vital military infrastructure. This military degradation precipitated a tangible decline in its political influence. Regionally isolated by the fall of its Syrian ally and unable to dictate terms domestically, facing the state signaling a potential shift in Lebanon's internal power dynamics.
Faced with military exhaustion, regional isolation, domestic political setbacks, and a core narrative of "resistance" severely challenged by the reality of defeat, Hezbollah confronts an existential crisis. The organization that emerged from the 2024 conflict is fundamentally different from the one that entered it. This analysis, probes the future trajectory of Hezbollah in this drastically altered landscape to understand how Hezbollah might adapt, survive, or transform in the face of these compounding pressures, and the constraints facing the Lebanese state and the United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL) in asserting sovereignty, the divergent perspectives shaping the political discourse, and the plausible future pathways for Hezbollah in Lebanon.
1 May 2025
Rajaee Port Explosions: Could it Disrupt Diplomatic Path Between Tehran and Washington?
The strategically significant Rajaee Port in Bandar Abbas, southern Iran, was rocked by a massive explosion during the third round of Iranian-US talks in Oman on Saturday, April 26 2025, marking a pivotal moment that warrants in-depth analysis. Located near the Strait of Hormuz, the port serves as a critical nexus for Iran's container traffic and plays a crucial role in the country’s foreign trade, especially amid the sanctions imposed on it. Initial reports point to two primary hypotheses regarding the cause of the incident: the first suggests an accidental explosion resulting from mishandling hundreds of tons of a vital chemical substance, likely used to fuel Iran’s ballistic missile programme, reminiscent of the 2020 Beirut explosion; the second, however, raises the possibility of deliberate sabotage, potentially orchestrated by Israel with the intent to disrupt the Iranian-American diplomatic track. The timing of the explosion, coinciding with intense diplomatic efforts, adds further weight to its potential ramifications.
Regardless of the final cause, an explosion of such magnitude exposes significant vulnerabilities in Iran's security and management systems, reverberating across the entire region. It casts a shadow over diplomatic efforts aimed at addressing nuclear tensions and other unresolved issues. This commentary explores the potential post-incident scenarios, the implications of each hypothesis
10 Apr 2025
Navigating the Thaw: Scenarios for the US-Iran Negotiations
The geopolitical landscape in the Middle East is set for a potentially major shift with US President Donald Trump’s announcement of the resumption of negotiations between the United States and the Islamic Republic of Iran, scheduled to begin on April 12, 2025. Following a period marked by escalating bilateral tensions and the effective dissolution of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), this resumption of dialogue has generated considerable anticipation both within Iran and across the wider region. The initial, albeit potentially transient, positive reactions observed in Tehran’s financial markets, as evidenced by movements in the stock market and gold prices, underscore the profound economic implications these discussions could hold for the Iranian populace. Furthermore, the potential for these negotiations to influence broader regional stability is a matter of significant concern and interest even for the nations within the Arabian Gulf. While the precise modalities of these diplomatic engagements – specifically whether they will entail direct bilateral talks, as suggested by the U.S. administration, or proceed indirectly through intermediary channels – remain subject to clarification, the very initiation of dialogue signifies a notable departure from the recent trajectory of U.S.-Iran relations. This analysis will therefore explore a range of plausible scenarios that may unfold as delegations from the United States and Iran convene on April 12, and consider the salient internal political dynamics within both nations, the prevailing external pressures exerted by regional and international actors, and the specific contextual factors that have contributed to this renewed, albeit cautious, engagement.
13 Mar 2025
Silent Annexation: The Fate of Southern Syria
Caught in the crosscurrents of escalating regional and international rivalries, and witnessing an increasingly assertive Israeli presence, Southern Syria stands at a critical juncture. Ambiguity hangs heavy in the air, obscuring the long-term trajectory of a land grappling with fractured governance, demographic shifts, and the looming threat of further fragmentation. As international and regional actors jostle for influence and advantage, Israel's expansionist ambitions in the south proceed with a disconcerting sense of ease, guided by a methodical strategy and far-reaching objectives. This expansion, however, is not merely territorial; it is reshaping the very fabric of Southern Syria, impacting its social and demographic tapestry, and transforming it into a volatile arena for regional proxy conflicts. Meanwhile, the Syrian state, nominally in Damascus, grapples with deep-seated internal divisions and a diminished capacity to exert meaningful control, potentially paving the way for negative scenarios that threaten the nation's already fragile unity and sovereignty. This analysis aims to dissect these complex transformations, illuminating Israel’s calculated strategy, assessing the internal vulnerabilities of Syria, and anticipating the potential risks that lie ahead for this strategically vital, yet increasingly precarious, region.
4 Mar 2025
A Troubled Chain of Command: Politics and the IDF
The appointment of Major General Eyal Zamir to the helm of the Israeli Army, will take office on March 6, transcends a routine leadership transition. It portends a potential strategic recalibration in Israeli military thinking, responding to evolving threats and perceived doctrinal vulnerabilities. Lauded across Israel's political spectrum as the right leader for these turbulent times, Zamir inherits a complex and precarious landscape. He is tasked with revitalizing an army perceived as "faltering," navigating a potentially obstructive political environment, and addressing a volatile region simmering with unresolved conflicts. Adding to the weight on his shoulders is the historical baggage he carries in the eyes of Palestinians, for whom his name evokes memories of harsh measures during past uprisings and operations. This analysis delves into the implications of Zamir's appointment, the delicate dance between political leadership and military autonomy in Israel, the anticipated doctrinal shifts under his command, and the spectre of looming confrontations on multiple fronts.
25 Feb 2025
Emergency Arab Summit: The End of Gaza’s Suffering?
The upcoming emergency Arab summit in Cairo on March 4, 2025, occurs amid widespread regional and global condemnation of U.S. President Donald Trump's proposal to "take over" the Gaza Strip, transform it into what he claims will be the "Riviera of the Middle East," and resettle Palestinians elsewhere. This plan, though predictably outlandish, catalyses a gathering fraught with both peril and potential as it introduced uncertainty into the delicate ceasefire negotiations between Israel and Hamas. There are growing concerns that it may derail discussions for the second phase of the truce, which seeks to end the 15-month-long war.
Cairo finds itself not merely hosting a summit, but rather presiding over a critical juncture, one that will test the very foundations of Arab solidarity and expose the vulnerabilities inherent in a region perpetually teetering on the brink. This summit is not simply about addressing the Palestinian issue; it is about confronting a blatant disregard for Palestinian rights and a cynical manoeuvre that threatens to unravel any semblance of regional stability.
The summit’s raison d'être is clear to construct a unified Arab front against this displacement agenda and, more broadly, to reaffirm a collective commitment to the Palestinian cause. However, the very notion of “Arab unity” is itself a historically fraught concept, often more aspirational than actual. Past summits have showcased deep divisions and diverging national interests, rendering collective action elusive. Cairo must navigate these fault lines, leveraging the palpable outrage over the displacement proposal to forge a genuine consensus. The challenge lies not only in articulating a unified stance but in ensuring its practical implementation, translating rhetorical solidarity into concrete actions. This summit will serve as a litmus test for the Arab League’s relevance and capacity to act as a cohesive force in the face of external pressures and internal fissures. The spectre of past failures looms large, demanding a demonstrable shift from pronouncements to tangible outcomes.
6 Feb 2025
Will Israel Suceed in Dissolving UNRWA During Trump’s Second Term?
In a significant escalatory move, Israel’s Ambassador to the United Nations, Danny Danon, has notified the UN Secretary-General in writing that UNRWA must cease its operations and vacate its premises by January 30, 2025. This ultimatum follows Israel’s enactment of a law last October banning the agency’s activities within its territory, including occupied East Jerusalem. The decision is rooted in Israel’s allegations that UNRWA has been infiltrated by Hamas, with claims that some of its employees were involved in the Oct. 7, 2023, attacks.
This paper examines the evolving and contentious relationship between Israel and UNRWA. It also explores potential U.S. intentions to dismantle the agency, particularly in light of Donald Trump’s return to power and his recent remarks regarding the displacement of Gaza’s population and the repercussions of this ban.
8 Jan 2025
Back to Square One: Will the Presidential Vacuum in Lebanon Come to an End?
Lebanese Parliament Speaker Nabih Berri reiterated his call for a general session of Parliament on Jan. 9, 2025, to elect a new president as Lebanon’s presidential vacuum stretches into its third year. This call comes amid an ongoing crisis that began on October 31, 2022, following the end of former President General Michel Aoun's term. Aoun’s departure marked the conclusion of a previous presidential vacuum that lasted for 29 months, during which 45 attempts to reach a quorum for his election were unsuccessful. In the current vacuum, Parliament has failed to elect a president after twelve sessions, the most recent of which was held on June 14, 2024. This series of unsuccessful attempts highlights the profound complexities of Lebanon’s political process.
Recent domestic initiatives aimed at resolving the presidential vacancy and reaching a consensus on a candidate have also faltered. Meanwhile, representatives from five key countries, the United States, France, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Qatar, continue their efforts to mediate and navigate the obstacles hindering Lebanon’s political forces from agreeing on a mechanism to address the protracted vacancy crisis.
Amid persistent uncertainty surrounding the identity of Lebanon’s next president, political circles have been actively circulating the names of potential candidates. Among these, Commander of the Lebanese Army General Joseph Aoun, has emerged as a strong contender and is widely viewed as a likely consensus candidate.
The upcoming parliamentary session has ignited significant hopes that it may produce tangible results and lead to the selection of a new occupant for Baabda Palace. However, this optimism is tempered by pressing questions about whether Lebanon’s political forces can overcome their divisions, resolve the presidential vacuum, and converge on a candidate amidst the shifting political dynamics within Lebanon and across the region.
25 Dec 2024
From Lebanon to Syria: How Did the Syrian Civil War Reshape Hezbollah’s Military?
Hezbollah's involvement in the Syrian Civil War has significantly bolstered its military capabilities and strategic positioning against Israel. The war served as an invaluable training ground, providing Hezbollah fighters with extensive combat experience and allowing them to test and refine their tactics in real-world scenarios. This experience proved crucial in enhancing their proficiency in asymmetric warfare, a critical aspect of their confrontations with the technologically superior Israeli military.
Furthermore, the Syrian conflict solidified Hezbollah's alliance with Iran, which provided vital military support and resources. This included advanced weaponry, training, and logistical assistance, significantly enhancing Hezbollah's operational readiness. Iran's backing also enabled Hezbollah to establish a stronger presence in the region, providing strategic depth and allowing it to operate more effectively against Israel while countering Israeli influence in Lebanon and the broader Levant.
The war also forced Hezbollah to adapt and evolve its military doctrine. The group adopted more sophisticated tactics, incorporating urban warfare strategies and integrating advanced technologies like drones and precision-guided munitions. These innovations, born out of necessity on the Syrian battlefield, have better equipped Hezbollah to counter Israel's military advantages. Moreover, the prolonged conflict forced Hezbollah to develop sophisticated logistical and operational planning capabilities, including a robust supply chain that can withstand Israeli disruptions.
On the other hand, this intervention led to the exposure of the party and made it vulnerable to infiltration, which caused the party to lose its hard power against Israel and its soft power within Lebanon.
18 Dec 2024
Mahabad: Oil, the Peshmerga, and the Collapse of the Kurdish Dream
The Kurdish dream of establishing an independent state was on the verge of realisation after centuries of demands in Jan. 1946. This came when “Qazi Mohammad,” the Iranian Kurdish leader, declared the establishment of the Mahabad Republic in the province of the same name, now part of the Islamic Republic of Iran. However, this dream quickly dissipated when the Soviet Union withdrew its financial support for the nascent state. The intensification of the economic blockade on the region further compounded the situation, preventing the entry of food supplies and reducing agricultural production. These pressures led to dramatic shifts in the loyalties of Kurdish tribal leaders who had initially allied with “Qazi” during the state's formation, hoping to secure a share of Soviet financial and food aid.
The food situation worsened over time, pushing some leaders of the Mahabad army to leave the capital, especially as Iranian forces were nearing its entrance, leaving the Kurdish leader and a small Kurdish group behind to face an unequal battle with the Iranian army. Therefore, to spare Kurdish blood, it was decided to surrender on December 15 of the same year, leading to the Iranian army's occupation of Mahabad and the declaration of the state's fall. In the end, “Qazi” was executed in March 1947, marking the end of the closest attempt to establish a Kurdish state.
About a quarter of a century later, the Iraqi Federal Supreme Court issued a series of rulings regarding Iraqi oil exported by the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. The latest ruling, issued in Feb. 2024, mandated the Kurdistan Regional Government’s Council of Ministers to hand over all oil and non-oil revenues to the central government in Baghdad. This could have a dual impact similar to that caused by the cessation of financial support and the Iranian blockade on the Mahabad army, but this time it affects the Peshmerga forces that represent the hope for preserving the “autonomy” of the Kurdistan Region of Iraq considered the second closest Kurdish attempt at establishing a national homeland for the Kurds.
Therefore, the First Part of this paper addresses the political situation of the Kurds, focusing on the status of the region in the Iraqi Constitution, the contentious issues between the region and the federal government, and the impact of these disputes on the continuity and existence of the Peshmerga. The Second Part reviews the economic situation, examining the effects of the series of judicial rulings on the conditions that undermine the autonomy of the regional government in selling oil and the repercussions of this on the Peshmerga as a Kurdish defence force that protects the “autonomy” of the region, forming the last line of defence against its collapse.
2 Dec 2024
Remontada?! How Will Syrian Armed Factions Redefine the Regional Landscape
On Wednesday, Nov. 27, 2024, Syrian armed factions launched a coordinated offensive targeting regime-controlled sites and militia positions in the western countryside of Aleppo, northern Syria. This operation marks the most significant joint military action since 2016, involving key groups such as “Hay'at Tahrir Al-Sham” (formerly Jabhat Al-Nusra). In a video statement, the Joint Operations Room declared the initiation of the “Deterrence of Aggression” operation. The announcement emphasised that the offensive was necessitated by recent regime movements threatening civilian areas, framing the operation as a defensive imperative rather than a strategic choice. The statement underscored that this action was in direct retaliation for the Syrian regime's bombardment of north-western regions, signalling a potential escalation in the conflict dynamics of the region.
19 Nov 2024
COP 29: Another Missed Opportunity for Action?
Despite a 2009 pledge to mobilise $100 billion annually by 2020, this commitment remains largely unmet, hindering adaptation and mitigation efforts. The 2015 Paris Agreement, while aiming to limit global warming, faces implementation challenges due to insufficient pledges and a lack of accountability. Developed countries, bearing historical responsibility for the climate crisis, must assume a leading role in mitigation and provide adequate financial support. Unfulfilled pledges perpetuate a cycle of vulnerability in the Global South, exacerbating the impacts of extreme weather events and rising sea levels. Climate change poses a challenge to sustainable growth in a number of industries and is not just an environmental concern. It is also an economic one. Insufficient investment for climate change exacerbates problems including growing debt in developing countries, decreased agricultural productivity, food insecurity, and volatility in sectors like tourism. These issues, which are linked to global accords like the Paris Agreement, are pressing and need to be addressed.
3 Nov 2024
Harris’s Hollywood vs Trump’s Evangelicals
As the U.S. election looms, former President Donald Trump and Vice President Kamala Harris are both working to mobilise their supporters, ensuring strong voter engagement by Election Day on November 5. While both campaigns employ similar tactics, the Harris campaign has followed recent Democratic strategy by leveraging celebrity endorsements to inspire younger voters, who historically have lower turnout rates but tend to lean Democratic. This challenge with young voters, contrasts with the Trump campaign’s stronger base among White Evangelicals, who, despite not making up a majority of the population, reliably vote in large numbers across the United States (U.S.). The Harris campaign’s reliance on Hollywood celebrities highlights the industry’s alignment with liberal causes and the need to mobilise young voters, compared to the consistent support Trump receives from conservative religious groups, who form a reliable voter base. The divide between Harris’s Hollywood and Trump’s Evangelicals is another representation of another dividing line in the U.S. and raises questions.
10 Oct 2024
BRICS BRIDGE: Will Russia Reshape the Global Financial Order?
The world is currently experiencing rapid and significant geopolitical shifts, with rising global powers like the BRICS Group leading the charge to recalibrate the balance of influence within the Global Financial System. The recent expansion of the BRICS Group, now including 10 nations following the accession of Egypt, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Iran, and Ethiopia, underscores their growing influence. This bloc is unwavering in its determination to challenge the dominance of the U.S. dollar and to overhaul a global financial infrastructure that it sees as deeply flawed. The BRICS nations argue that the current system, with its structural flaws, serves as a tool for exerting political and economic pressure and contributes to the fragmentation of economies and regions by weaponizing trade and financial constraints.
The BRICS+ nations acknowledge that Dollar Dominance is underpinned by entrenched factors, most notably, the U.S. military power and global confidence in the U.S. legal and regulatory frameworks. Nevertheless, these nations are actively exploring alternatives to reduce their reliance on the dollar, aiming to bolster their financial sovereignty.
In pursuit of this goal, BRICS has ramped up efforts to reduce dependence on the dollar by employing innovative mechanisms. Chief among these is the proposal to issue a new, collective currency and establish a multilateral digital settlement and payment platform, dubbed as the “BRICS Bridge.” This platform is poised to foster greater trade integration among member states, particularly as some nations within the bloc, like Russia, face sanctions and exclusion from global systems such as the SWIFT System -The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication-.
All eyes are now on the upcoming BRICS Summit, set to take place in October in Kazan. The summit is expected to showcase tangible steps toward implementing these initiatives, which could potentially redefine the structure of international trade and finance. The critical question remains: Will Russia and its BRICS allies break the dollar's stranglehold over the global financial order?
5 Oct 2024
A Year of War on Gaza: Who Loses and Who Gains?
The Israel-Hamas War has now entered its second year following the unexpected assault by Palestinian factions on Israel on October 7, 2023. This sudden attack disrupted Israel’s long-held sense of security, undermining public confidence in both the Israeli military and its intelligence apparatus. In response to the incursion, the Israeli military launched a devastating offensive on Gaza, resulting in over 41,500 fatalities and leaving 96,000 others wounded Moreover, a punitive blockade has severely cut off essential supplies of food, energy, water, and medicine, crippling Gaza’s already fragile healthcare system. The blockade, coupled with ongoing military strikes, has devastated key infrastructure, housing, the economy, agricultural lands, and fishing fleets. This has pushed nearly half a million people into a state of food insecurity.
Israel has consistently forced Gaza’s residents to relocate into increasingly confined areas, with the number of displaced individuals now reaching nearly 1.9 million. The widespread devastation has led the United Nations to issue repeated warnings, cautioning that Israel’s actions are rendering Gaza uninhabitable.
After a year of war, Israel has failed to achieve its primary objectives. Hamas remains intact, and the prisoners held by its factions have not been released. Instead, the war has widened, with violence escalating beyond Gaza and into the West Bank, while tensions between Israel and Iran, along with its regional proxies, have intensified. This escalation has pushed the Middle East to the brink of a broader confrontation, potentially setting the stage for a full-scale war between Israel, Iran, and its respective proxies. As hopes for a ceasefire and prisoner exchange dwindle, pressing questions now emerge: Who stands to lose and who will benefit from this protracted war? When and how will Israel’s war conclude, and what will be left in its wake?
This analysis highlights the gains and losses of the most important parties to the conflict as follows:
18 Sep 2024
Restoring Lost Deterrence: Pager Explosions in Lebanon
In a well-coordinated assault targeting Lebanon’s southern suburbs—an area known for being a Hezbollah stronghold—and specific regions in Syria, hundreds of pager devices used by Lebanese Hezbollah members were detonated simultaneously. Early reports, at the time of writing, suggest the attack claimed the lives of over a dozen individuals and left thousands more injured.
Israel has a long-established record of carrying out extrajudicial operations, ranging from targeted assassinations to sophisticated cyber-attacks aimed at its adversaries. A hallmark of its tactics includes booby-trapping communications devices, as seen in the 1996 assassination of Yahya Ayyash, a prominent Hamas bomb maker, who was killed using a bomb concealed within his mobile phone. Given this precedent, it is plausible that Israeli intelligence, specifically the Mossad, orchestrated the recent operation by infiltrating the manufacturing process of these pager devices, possibly embedding lithium-ion batteries rigged with meticulously calibrated explosives.
The operation raises many questions about the strength of the security of Hezbollah’s communications infrastructure, which calls for looking at the incident from a deeper perspective to decipher its meanings and implications from the perspective of the communications security used by Hezbollah or other resistance groups in the region or even regular armies in the Middle East.
11 Sep 2024
Al Karamah Crossing Incident: Individual Act or Growing Resistance?
A Jordanian citizen opened fire at the Al Karamah crossing—known as the King Hussein Bridge in Jordan and the Allenby Bridge in Israel—resulting in the deaths of three Israeli security guards. This incident took place in a commercial zone under Israeli control, where Jordanian trucks unload goods bound for the West Bank. While the crossing has seen relatively few security breaches since 2014, when Israeli guards fatally shot a Jordanian judge they claimed had attacked them, this latest episode marks a significant and potentially destabilising development.
The timing is particularly notable. The current incident marks a significant and troubling development, being the first of its kind since the events of October 7, which triggered the Israel-Hamas war and escalated tensions across the region. Its occurrence comes amid heightened Israeli military operations, including a nine-day incursion into the city of Jenin and its adjacent refugee camp in the West Bank.
Israel’s immediate response was to seal all land crossings with Jordan, halting civilian passage and initiating investigations into the Jordanian trucks present at the time of the attack. This blockade has resulted in significant logistical disruptions, with dozens of convoys stranded at the border. The incident not only exacerbates regional tensions but also prompts critical questions: Is this an isolated incident, or does it represent the fuse for a broader wave of resistance against Israeli policies in the occupied territories?
10 Sep 2024
The Silent Rise: How China is Changing the Middle East
China has mediated a Palestinian reconciliation dialogue in Beijing, and has succeeded in bridging the rift between Saudi Arabia and Iran. These steps indicate a change in China's approach to the Middle East, as it has become an active player in the region by expanding its policies to include political and strategic considerations, in addition to its energy interests. Its "non-interventionist" policy has attracted many countries in the region, which see their growing relations with Beijing as a means of diversification. However, China's increasing involvement may pose a threat to US interests in the region. As Washington has increasingly focused on the Indo-Pacific region, China has emerged as an active player in the Middle East, reshaping regional security dynamics, signing strategic partnerships and memoranda of understanding for its economic activities with most Middle Eastern countries, and strengthening its ties with various regional organizations over the past two decades. Recent Chinese diplomatic initiatives demonstrate Beijing’s deep investment in further developing relations with Middle Eastern countries, with Beijing hosting the Arab-Chinese Summit and the Gulf-China Summit, demonstrating its commitment to strengthening strategic partnerships among the region’s countries and promoting economic development beyond its traditional energy interests. China’s growing engagement in the Middle East is seen as a significant factor shaping the region’s geopolitical landscape and has significant implications for global politics. This raises the question: how China’s methods diverge from those of the United States (U.S.) in the region?
5 Sep 2024
El-Sisi’s Visit to Ankara: A Key Diplomatic Move During Unrest
In a move with significant political and economic implications, Egyptian President Abdel Fattah El-Sisi embarked on an official visit to Ankara Sept. 4, 2024. This highly anticipated visit comes months after Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan's visit to Egypt earlier this year and his invitation to President El-Sisi to Ankara. The current visit, considered a turning point in Egyptian-Turkish relations, aims to strengthen bilateral cooperation and open new avenues for coordination on regional and international issues. After a decade of tension and estrangement in the relations between Egypt and Turkey.
The Egyptian President's visit to Turkey is of special importance, as it is the culmination of a long phase of discussions aimed at restoring relations between Egypt and Turkey to their normal course. The rounds of talks and meetings concluded with Erdogan's visit to Cairo last February, which witnessed the announcement of the revival of the High-Level Strategic Cooperation Council for relations between the two countries in its new form, where both leaders co-chair the first meeting of the Council. The meeting also involved a comprehensive review of the Egyptian-Turkish bilateral relations and discussions on potential steps to further enhance the Egyptian-Turkish cooperation.
This analysis highlights the motivations of this visit and its implications on regional and Turkish politics.
3 Sep 2024
Political Consequences of Germany’s Local Election
More than three decades after the fall of the Berlin Wall, Germany’s political divide between East and West persists, casting a long shadow over national unity. In the eastern regions, political tensions have heightened, culminating in a pivotal moment during the Sept. 1, 2024, local elections. The far-right Alternative for Germany (AfD) party secured a historic win, achieving 33% of the votes in Thuringia, making it the strongest party in the state. In Saxony, it placed second with 30%, trailing only the centre-right Christian Democratic Union (CDU). Despite repeated warnings labelling the AfD as extremist and even Nazi-aligned, it has exploited the disenfranchisement in the East, filling the political void left by the ruling coalition. Its local success forms part of a broader strategy aimed at normalising its extremist rhetoric as it eyes a climb to national prominence. The potential consequences of the AfD's rise to national prominence are significant, reshaping Germany’s political landscape in ways that could have far-reaching implications.
22 Aug 2024
Recurring Patterns: How Will Iran Respond to Ismail Haniyeh’s Assassination?
The world has been on edge since July 31,2024, awaiting Iran’s response to the assassination of Ismail Haniyeh, head of the Hamas political bureau, in Tehran by an Israeli attack. Haniyeh was targeted while attending the inauguration ceremony of Iranian President Masoud Pezekshian, marking a direct challenge to Iranian sovereignty and its role as a regional leader of resistance movements. This event underscores the broader confrontation between Iran, which opposes what it perceives as the United States and Israeli dominance in the region. Given the assassination's symbolic and strategic significance, many see Iran’s retaliation as inevitable, particularly amid escalations between Israel and Iran. Notably, this incident is part of a broader series of high-profile killings targeting figures within the so-called resistance axis. Just hours before the explosion in Tehran, Israel launched a missile strike in Beirut's southern suburbs, killing Fouad Shukr, a senior Hezbollah military official, while also claiming—without confirmation—the assassination of Mohammed Deif, a leading Hamas military commander.
While consensus exists regarding the certainty of an Iranian response, there is sharp debate within political and military circles over the nature of this retaliation. The targeted nature of the Israeli strikes suggests that a direct and immediate Iranian response may be needed to restore its deterrent credibility. However, Iran’s extensive network of regional proxies presents an alternative, allowing Tehran to retaliate indirectly while avoiding the military and economic costs of direct confrontation. This calculation has become more critical following the U.S.’s declaration that it would militarily defend Israel against any Iranian attack, reaffirming its earlier stance on Iranian missile strikes against Israel in April.
Predicting the nature of Iran’s response can be facilitated by examining the pattern of its previous reactions to similar attacks, particularly given Iran’s long history of confrontations following the 1979 revolution and its enduring hostility toward the U.S. Among these conflicts, the one most analogous to the current situation is the so-called Tanker War, which took place between Iran and Iraq from 1984 to 1988. Iran successfully drew the U.S. into a large-scale military engagement in the Arabian Gulf during this period. This scenario holds significant parallels to today’s tensions, as will be detailed later.
This paper, therefore, aims to analyse the similarities and differences between Iran’s current posture and its stance during the Tanker War from multiple perspectives—military, political, and economic—both internally externally. By comparing the dynamics at play, including the role of the U.S. in both scenarios, this analysis seeks to clarify what can be expected from Iran in light of these combined variables.
15 Aug 2024
Syria-Turkey Normalisation: Are Yesterday’s Enemies Today’s Friends?
Since the eruption of the Syrian Civil War in 2011, several countries have cut diplomatic relations with Syria turning Damascus into a pariah state. 13 years later, the shifting regional geopolitical landscape appears to be ushering in a new reality. Today, both regional and global powers are moving toward rapprochement with Syrian President Bashar Al-Assad’s regime. In a significant U-turn, Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan, once a staunch opponent of Al-Assad, is now seeking normalization with Syria. While, Turkey is not alone in this effort, Syria's potential reintegration could have far-reaching implications.
4 Aug 2024
Iranian Influence in Sudan: Balancing Drone Diplomacy and Conflict Pressures
Relations between Sudan and Iran have experienced a volatile history of rapprochement and estrangement over the past eight years, mainly due to the strong tensions between the two countries. The relationship was notably strained after Iranian protesters stormed the Saudi embassy in Tehran in 2016, prompting the Sudanese government to close all Iranian schools and cultural centres. However, amid escalating regional tensions between Tehran and its supporters on one side and Washington and its allies on the other, Sudan and Iran are moving quickly to open a new chapter in their relations. This development comes against the backdrop of the ongoing war between the Sudanese army and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces since April 2023.
The current regional changes have created an opportunity for Sudan and Iran to address past differences in a calculated manner. Relations have shown noticeable growth over the past year, marked by a series of high-level official meetings between Sudanese and Iranian officials. One significant meeting took place on the sidelines of the Non-Aligned Movement Ministerial Committee meeting in the Azerbaijani capital, Baku, in July 2023, where former Sudanese Foreign Minister Ali Al-Sadiq, met with his Iranian counterpart, Hossein Amir-Abdollahian. This meeting signalled a rapprochement, culminating in Sudan’s announcement of the official resumption of its diplomatic relations with Iran Oct. 9, 2023.
A year after the resumption of relations, the Chairman of the Transitional Sovereignty Council, Abdel Fattah al-Burhan, received the credentials of the Iranian ambassador, Hassan Shah Hosseini, July 21, 2024, appointing him as his country’s ambassador and plenipotentiary to Sudan. This move raised many questions, particularly due to its timing, which coincided with escalating regional tensions and months of ongoing battles between the Sudanese army and the Rapid Support Forces. Additionally, it occurred in the context of the normalisation of relations between Khartoum and Tel Aviv, which began approximately four years ago.
This rapprochement raises many questions about the agreement’s sustainability, particularly given the two countries’ divergent regional priorities. While Iran focuses on the Gulf and the Arab Levant, the future of this relationship hinges on regional developments and Iran’s strategic calculations in the Red Sea region. Will the ties radically shift toward a sustainable strategic partnership or remain captive to regional tensions and political tactics?
31 Jul 2024
The Assassination of Ismail Haniyeh: Implications for the Region
Ismail Haniyeh, the leader of Hamas’s political bureau, was assassinated in Tehran, Iran on July 31, 2024, following his attendance of the inauguration of Iran’s new president. Iran and Hamas have accused Israel of the assassination but Israel has given no response, as is common practice when Israel is involved in an assassination. The assassination of Haniyeh followed the earlier killing of Fuad Shukr a senior Hezbollah commander in Beirut by Israel, as retaliation for an attack that left 12 dead in the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights.
Israel has stated previously that it would target Hamas officials wherever they are following October 7, and were successful in December when they assassinated Haniyeh’s deputy in Beirut, which brought ceasefire talks to a halt.
The targeting of Haniyeh who was leading negotiation efforts for a ceasefire in the Israel-Hamas War is a serious escalation, and its occurrence in the heart of Iran directly following the inauguration of Iran’s president, not only has serious implications on the Israel-Hamas War, but for Iran and its proxies as well, who have been targeted recently by Israel.
So far, Iran has not provided information on how the assassination occurred, with the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) stating that the attack is under investigation, it is likely that a precision guided missile was used to target the IRGC veteran’s mansion that he was staying in. Following the assassination, Iran's Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, has pledged that Israel will face "harsh punishment" for its action in Tehran.
This is not the first time that Israel has been able to penetrate Iran’s borders to conduct assassinations, Israel has routinely been able to target Iranian officials such as its yearslong assassination campaign against Iranian nuclear experts and others involved in the Iran’s nuclear program. Most recent was the 2020 assassination of, Mohsen Fakhrizadeh, a leading Iranian military nuclear scientist, was killed by a remote-controlled machine pistol while driving outside Tehran.
Given Iran's direct and massive missile barrage against Israel in April, following the bombing of its embassy in Damascus, the world now faces significant questions: How will Tehran respond to the assassination of Ismail Haniyeh on its soil? Moreover, does Iran have the capability or incentive to contain the actions of Hezbollah and the Houthis, especially after Israel’s killing of Hezbollah’s Fuad Shukr in Beirut and its bombing of the Houthi’s Hodeidah Port?
28 Jul 2024
Unpacking the Majdal Shams Attack
The Israel-Hamas War has fundamentally altered the dynamics of engagement between Israel and Hezbollah. Before October 7 the two adversaries adhered to a set of engagement rules established after their 2006 conflicts, which restricted their military actions to specific areas like the Shebaa Farms, avoiding deeper incursions into each other's territory. However, over the past nine months, these rules have eroded, leading to an escalation that, while intense, has not yet escalated into full-scale war.
In October 2023, Hezbollah escalated its involvement by launching rockets into Israeli-occupied territories. This marked a significant shift, with both parties engaging in psychological warfare, openly sharing or hinting at intelligence about each other. Hezbollah’s actions soon expanded to include strikes deeper into Israeli territory. In response, Israel targeted Hezbollah military installations near the Israeli-Lebanese border. It conducted a series of targeted assassinations of leaders within the elite Radwan Division, which oversees operations near the border. Israel’s retaliatory measures have since broadened to encompass a wider area of southern Lebanon and the Bekaa Valley, indicating a significant escalation in the conflict dynamics.
The conflict further escalated to encompass the village of Majdal Shams, a Druze village in the Golan Heights. The Israeli military spokesperson reported that a rocket targeting the village was an Iranian-made Falaq-1, launched from the area north of Shebaa in southern Lebanon, with Hezbollah allegedly responsible for the attack.
According to the Israeli account and preliminary investigations, the missile was indeed launched from Lebanese territory, specifically the Shebaa Farms. However, it was not intended to strike Majdal Shams; an Israeli missile interception redirected it, causing it to land in the village.
21 Jul 2024
The Power of the Word: How the UAE Redefined International Mediation?
The 21st century has witnessed a resurgence of mediation as a pivotal tool for resolving international disputes. This resurgence is driven by the complexities of contemporary conflicts and the expansion of threats beyond traditional regional conflicts, civil wars, and political crises. The scope of security threats now includes issues such as climate change, cybersecurity, and transnational organised crime.
Several countries have played significant roles in mediation, leveraging their diplomatic acumen, political influence, and economic resources to facilitate dialogue and prevent escalation. Norway has consistently demonstrated its commitment to peacebuilding through active participation in resolving conflicts among the most prominent mediators. From Sri Lanka to Colombia and the facilitation of the Oslo Accords, Norway has embodied its ability to promote dialogue between seemingly irreconcilable adversaries.
Known for its multilateral approach and emphasis on consensus building, Finland initiated the Group of Friends of Mediation in September 2010, significantly contributing to peace processes in the Horn of Africa. Similarly, Switzerland, with its long-standing tradition of neutrality, has provided a safe and neutral venue for countless peace talks and negotiations, fostering an environment conducive to compromise and resolution.
Amid the resurgence of mediation in international diplomacy, the last decade has witnessed the emergence of non-Western actors in this field. At the forefront is the United Arab Emirates (UAE), which has become an essential player in the Middle East and beyond. Since its founding, the UAE has combined traditional Arab values with modern diplomatic practices to address the cultural complexities of regional conflicts, adopting a policy of promoting peace, security, and stability both regionally and globally.
The UAE’s commitment to mediation is evident in its numerous initiatives aimed at calming conflicts and crises, including active mediation in the ongoing conflict in Yemen, facilitating dialogue and humanitarian aid, playing a crucial role in reconciliation efforts between India and Pakistan; its pivotal role in the historic 2018 peace agreement between Ethiopia and Eritrea, marking a significant achievement in regional stability; facilitating prisoner exchanges between Russia and Ukraine, showcasing the UAE's diplomatic reach; mediation efforts between Russia and the United States (U.S.), further highlighting the UAE's influence; and hosting the COP28 Climate Conference in Dubai, underscoring the UAE's active participation in global diplomacy.
However, the path to mediation is fraught with challenges. The inherent complexities of many regional conflicts, the conflicting interests of the parties involved, and the need to balance mediation efforts with national interests can hinder the achievement of sustainable solutions. Additionally, maintaining neutrality in polarised situations, limited influence over non-state actors, and potential capacity constraints are challenges that the UAE must overcome to ensure the continued success of its mediation efforts. Hence, the UAE’s role as a rising international mediator, focusing on the factors that enabled its rise, its mediation strategies, and the impact of its efforts on regional and global conflicts will be examined.
8 Jul 2024
BRICSPHONE: A Cultural Call to Unity to End Western Hegemony
The roots of Western cultural hegemony trace back to the age of European colonialism in the 15th century, a period marked by the forceful imposition of Western languages, norms, and customs upon the colonised world. This legacy, often violent and disruptive, marginalised local cultures and established a global hierarchy dominated by Western values. The 20th century saw this dominance amplified with the rise of the United States as a global superpower, where Western cultural hegemony took on a new dimension. American popular culture, including Hollywood films, music, and television shows, became ubiquitous worldwide. The English language cemented its position as the lingua franca of international business and communication. However, in an era increasingly defined by interconnectedness and cultural exchange, the emergence of BRICSPHONE signifies a potential paradigm shift. This initiative seeks to amplify the voices of non-Western cultures, challenge the prevailing narrative, and build a more inclusive, multipolar cultural landscape. This article explores the BRICSPHONE initiative and its potential to reshape the global cultural conversation, redefining cultural power and promoting a more diverse and representative cultural landscape.
27 Jun 2024
Iran’s Presidential Election: Intense Competition and High Stakes
Iranians are voting in a snap presidential election on June 28, following the sudden death of President Ebrahim Raisi in a helicopter crash in May. This situation is not unprecedented for the Iranian regime, which has faced similar scenarios. In 1981, Iran’s first president following the Islamic Revolution Abolhassan Banisadr, was removed from office by the Islamic Consultative Assembly for political incompetence. Later that year, his successor, President Mohammad-Ali Rajai, was killed in a suitcase bombing. Thus, the current political and constitutional vacuum is not new to Iran. This pattern of instability has occurred twice before during significant periods of political upheaval.
Ebrahim Raisi was one of the few figures who enjoyed the trust of the security establishment and the regime's cleric guards. He was expected to oversee the rise of a new supreme leader after the death of Ali Khamenei or perhaps become the supreme leader himself. Therefore, Raisi's death poses a significant challenge to the mullahs' regime, especially given the internal and external challenges that Iran has faced recently.
On the other hand, Iran’s Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei paved the way for the presidential elections by selecting only six candidates who passed the examination conducted by the Guardian Council. This council, comprising 12 clerics appointed by the Supreme Leader, nominated by the judiciary chief, and approved by parliament, filtered the candidates based on loose criteria that it interprets and explains. Out of 80 candidates who applied for the position, only these six were allowed to run, with the Guardian Council having the final say in choosing or excluding candidates.
For instance, while the Iranian Constitution does not explicitly bar women from running for president, the Guardian Council effectively prevents them from doing so. Despite four women registering candidacies in the current and past 13 presidential elections, none have been approved.
Article 115 of Iran’s Constitution requires the president to be “a politician and cleric of Iranian origin, an Iranian citizen, a director and a wise man, who enjoys a good reputation, honesty, and piety, and believes in the foundations of the Islamic Republic of Iran and the official religion of the country.” Additionally, criteria related to administrative capabilities are considered. Beyond these criteria, it is widely believed that Khamenei favours a loyal and conservative president who aligns with his views and adheres to the principles of the regime, including obedience to the Supreme Leader.
Therefore, this analysis aims to clarify the significance of these elections, the management process, and the priorities that voters and the regime seek in the next president.
26 Jun 2024
BRICS Experts Forum 2024 “The Role of the BRICS in the Search for a New World Order”
The 2024 BRICS Expert Forum was held during the Saint Petersburg International Economic Forum from June 5 to 8, 2024. This forum is a prominent event that brings together a diverse group of experts, policymakers, and thought leaders from around the world. It served as a pivotal platform for in-depth discussions and strategic dialogues on the growing role of the BRICS countries in shaping the course of global governance and multilateral cooperation. The BRICS Expert Forum provided a unique opportunity to analyse the challenges and opportunities facing the BRICS bloc in the context of a rapidly shifting global landscape and served as a catalyst for new thinking and innovative solutions to the complex issues facing the world today by promoting the dynamic exchange of ideas between experts from different backgrounds.
Mostafa Ahmed, senior researcher at the Political Unit from the Al Habtoor Research Centre, participated as a speaker in a discussion session entitled “Promoting Growth Through Partnerships, Jointly Exploring Paths to Modernisation” which focused on the dimensions of economic and cultural cooperation of the BRICS group.
It is worth noting that the forum expanded its scope beyond traditional membership in BRICS, as it embraced representatives from new members such as the United Arab Emirates, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Ethiopia. This widespread participation not only underscored the growing influence of these countries on the global stage but also highlighted the growing attractiveness of the BRICS model as an effective alternative to Western economic and political frameworks.
30 May 2024
The Modi Effect: Prospects and Challenges of a Third Term
Indian legislative elections were held on April 14, 2024, to choose a new parliament to represent the country for the next five years. These elections are considered the largest and longest in the world, given the vast geographical area of India, as voting will be held in seven phases across different states over a period of approximately six weeks. About 969 million voters will participate in these elections to choose 543 members of the lower house of the Indian Parliament (Lok Sabha). These elections are of great importance and are among the most expensive in the world, with their cost expected to reach be nearly double what was spent in the 2019 elections.
An opinion poll conducted by the Centre for Research and Studies of Developing Countries indicates that the ruling Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) is likely to win the 2024 Indian parliamentary elections, paving the way for a third term for Prime Minister Narendra Modi. The Lok Sabha elections are being held in a negative atmosphere, with opposition allegations of unequal playing field, as a result of the intervention of federal law enforcement agencies who have attacked several political leaders and froze their bank accounts for six weeks. This means that the elections will have political and economic repercussions if Modi wins a third term, which will in turn impact India’s internal situation.
22 May 2024
ASEAN’s Lessons: A Blueprint for Peace in the Middle East
This article was originally published on Ahram Online on May 21, 2024.
Southeast Asia's history, marred by prolonged conflicts since the 1950s, offers pertinent lessons for strife-torn regions seeking stability. The spectre of the Cold War transformed countries like Vietnam into battlegrounds for over two decades, pitting communist and capitalist ideologies in a gruelling contest. Laos, too, bore the scars of proxy warfare, enduring a protracted struggle between the communist Pathet Lao forces, backed by a sizable contingent of North Vietnamese troops of Laotian descent, and the royal government, in a conflict that spanned more than two decades.
20 May 2024
What’s Next for Iran?
On May 19, while returning from the inauguration of the Giz Galasi Dam, Iranian President Ebrahim Raisi’s helicopter crashed near Varzaqan, Iran. Initially described as a “hard landing” it became apparent by the end of the day that there were no survivors. The crash killed all on board, including President Raisi and Foreign Minister Hossein Amir-Abdollahian.
19 May 2024
The Politicisation of EU Corruption
The European Parliament (EP) has been embroiled in a series of corruption scandals, raising questions about the integrity of EU institutions. These events have led to increased scrutiny of lobbying activities, conflicts of interest, and the "revolving door" phenomenon. As the June EP election approaches, the scandals have further fueled anti-establishment sentiments and could potentially impact the election outcome.
“I appeal to you to resist the temptation to exploit this moment for political gain.”
A statement made in December 2022 by Roberta Metsola, President of the European Parliament (EP), in response to one of the bloc’s biggest corruption scandals, reveals a larger story about the politicisation of corruption in European politics.
22 Apr 2024
The War on TikTok: Security Concerns and Anti-Semitism
Social media has played a pivotal role in reshaping the narratives of the Palestinian-Israeli conflict since the outbreak of Oct. 7. The dissemination of news and information now extends far beyond traditional media outlets. Instead, social media platforms have emerged as potent influencers, surpassing the resonance of weapons and delineating a global divide between Israel and Palestine. These platforms have become arenas of contention, with users segregating into supporters and opponents, rendering them susceptible to content-related pressures amid the war. The war on Gaza has once again thrust TikTok into a heated discourse regarding the application's dangers and impact as a global forum for ordinary individuals to voice their opinions while also serving as a battleground for political factions to vie for narrative control. This debate assumes added significance as the audience of traditional news outlets continues to dwindle.
Recently, numerous TikTok videos concerning the war on Gaza garnered widespread attention, accompanied by pro-Palestinian hashtags, prompting Israeli President Isaac Herzog to engage in discussions with TikTok executives in February 2024. Expressing apprehension over the surge in antisemitic content on the platform since the onset of the Israeli war on Gaza, they assured President Herzog of their commitment to address the issue in the future. In a related context, social media companies based in the United States have already demonstrated a readiness to censor pro-Palestinian content. Human Rights Watch, in its December 2023 report, documented over 1,050 instances of content removal and suppression on Instagram and Facebook by Palestinians and their supporters between October and November 2023.
In this context, U.S. legislators, conservative activists, and technology investors have voiced calls to ban TikTok in the U.S., citing escalating concerns. These calls gained significant traction on March 13, 2024, when the U.S. House of Representatives overwhelmingly voted in favour of a bill. The bill places ByteDance, the parent company of TikTok, with two options, both fraught with implications: either sell the application to a U.S.-based company or confront a ban on distribution through significant platforms and application stores. President Joseph Biden voiced his backing for the bill and signalled his readiness to sign it into law pending Senate approval. However, the U.S. initiative this time brings forth broader concerns beyond national security, encompassing the application's ramifications on Israel's reputation. The country's standing has been damaged due to the swift dissemination of content depicting Israel's crimes against civilians in the Gaza Strip.
This analysis aims to elucidate the reasons behind the shift in the U.S. perspective on TikTok, moving from security concerns to the perception of promoting antisemitism. What repercussions would the embargo have on both the United States and Israel?
17 Apr 2024
The Fallout of Escalating Iranian-Israeli Tensions
The Iranian Revolutionary Guard's Air Force made a historic move by launching a direct assault on Israel in an operation dubbed "The True Promise," marking the first instance of such an attack originating from Iranian territory. Late on Saturday, April 13, 2024, Israeli cities were subjected to a relentless barrage of drones and ballistic missiles, signalling a significant escalation in tensions between the two nations. This offensive action follows Iran's earlier pledge to retaliate against Israel for its targeting of the Iranian consulate in Damascus, an incident that resulted in the deaths of seven Revolutionary Guard members, including two high-ranking leaders, on April 1.
This calculated escalation underscores Iran's unwavering commitment to defending its sovereignty and national interests while bolstering regional security. The global spotlight now shifts to the scale, sophistication, and broader implications of Iran's strike against Israel.
The Iranian assault on Israeli soil marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing conflict between the two adversaries, thrusting their hostilities from the shadows into the open arena of direct confrontation.
Against this backdrop, the Israeli response hinges on several key factors. Firstly, the extent to which Iranian proxies, such as the Houthis and Hezbollah, may actively participate in the conflict will influence Israel's strategic calculus. Secondly, the response will be shaped by the presence or absence of casualties among Israeli forces, as well as the effectiveness of its defence systems, bolstered by support from the United States, in mitigating potential damage. Lastly, how Israel opts to retaliate will be of paramount importance in determining the trajectory of the conflict.
Consequently, this analysis aims to elucidate the attack's ramifications and its economic repercussions on the parties involved in the conflict.
22 Mar 2024
Will Netanyahu Conscript the Haredim?
This article was originally published on Ahram Online on Mar. 22, 2024.
The question of conscripting Ultra-Orthodox Jews, commonly known as Haredim, into the Israeli military has once again taken centre stage. This resurgence in debate follows calls by secularists, supported by several war cabinet members, including Defence Minister Yoav Gallant. During a press conference on Feb. 28, they advocated for amending conscription laws to include the Haredim.
The urgency behind these calls is fuelled by various challenges Israel currently faces. These include a labour shortage exacerbated by the ongoing Israel-Hamas War and tensions along the northern border with Hezbollah. The potential inclusion of Haredim in military service has sparked significant controversy within the Haredi community. Chief Sephardi Rabbi Yitzhak Yosef even issued a warning of a mass exodus of Haredi Jews from Israel if conscription becomes mandatory.
This latest call reignites an enduring conflict within Israeli society, rooted in the exemption privileges historically granted to Haredim. The issue remains unresolved due to the influence of religious parties, the political considerations of prime ministers, and the social dynamics within Israeli society. The exemption policies have long been a contention, particularly among secular citizens. Tensions escalated during the costly mobilisation efforts for the Israel-Hamas War, with over 66,000 Ultra-Orthodox youths exempted from military service in 2023 alone. This disparity has led to increased demands for the inclusion of Haredim in the military service, especially given the multiple security threats faced by Israel since Oct. 7.
Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu's return to power in late 2022 alongside the right-wing bloc underscored their determination to challenge conscription policies. Netanyahu's efforts to amend the Judicial Authority Law, dubbed "judicial reform", were met with widespread opposition from the secular community, leading to massive demonstrations.
These amendments aimed to circumvent a 2017 Supreme Court ruling that invalidated legislation preventing Haredim's conscription. Despite government concessions, including multiple deferments of recruitment deadlines, the issue remains unresolved. As the latest extension is set to expire on Mar. 31, a looming question remains: Will Netanyahu conscript the Haredim?
3 Mar 2024
What if the U.S. Ceased Providing Military Aid to Israel?
A recent statement from the European Union Foreign Policy Commissioner, Josep Borrell, urging Israel's allies, notably Washington, to cease supplying weapons to Israel has ignited widespread controversy. This call comes amid heightened concerns over the significant civilian deaths in the Gaza Strip. Coinciding with this plea, a Dutch appeals court decision has prohibited the export of all spare parts for F-35 fighter jets destined for Israel. These developments unfold against the backdrop of Israel's plans to initiate an expanded military operation in Rafah. Such an operation raises the spectre of a potential humanitarian catastrophe, particularly concerning the over 1.3 million displaced individuals from the Gaza Strip who have sought refuge in Rafah since the commencement of military activities in the enclave.
The United States provides Israel with annual military aid worth $3.8 billion, which stands as one of the most substantial military aid packages supplied by the U.S. to any country globally. This commitment was reaffirmed by U.S. officials, including President Joseph Biden, who, during his tenure as Vice President under Barack Obama, emphasised the enduring strategic alliance between the two countries. Then Vice President Biden said the U.S. commitment to Israel transcends moral obligations and is a deeply rooted strategic obligation. During a visit to Tel Aviv amid the events of Oct. 7, he underscored that “the existence of an independent and secure Israel within globally recognised borders aligns with the practical strategic interests of the United States.” He further emphasised, “I have long said: If Israel didn't exist, we would have to invent it.” Evidence of the depth of relations and continued support is further demonstrated by Congress' approval of an additional $14.1 billion in military aid to Israel. This aid is intended to bolster Israel's capabilities in its conflict with the Hamas movement, specifically by providing air and missile defence support and replenishing U.S. military stock granted to Israel. This level of support echoes the assistance provided by the United States to Israel during the October 1973 War with the Egyptian Army.
The generous and unconditional support provided by the U.S. to Israel prompts numerous inquiries, particularly in the context of the U.S.'s inability to exert pressure on Israel to stop its war on Gaza. Additionally, its loss of control over the right-wing government's decision-making process regarding the potential expansion of the war to include Rafah, portending an imminent conflict with Egypt. Hence, this analysis endeavours to address a pivotal question: Will these developments prompt a shift in the U.S. stance toward Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and his right-wing government, potentially leading to a withdrawal from the notion of an expanded operation in Rafah? Furthermore, can the United States feasibly cease its military aid to this strategic ally in the Middle East?
5 Feb 2024
Navigating the Two-State Solution: Balancing Possibility and Hope in the Palestinian Cause
The Palestinian-Israeli conflict stands as one of the world's most intricate and pressing issues, marked by enduring conflicts between Palestinians and Israelis, with potentially dire consequences that could escalate into a regional war. In 1993, both Yasser Arafat, leader of the Palestine Liberation Organisation, and Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin embraced the two-state solution, leading to the signing of the Oslo Accords. The essence of these agreements aimed at establishing two states, one for Palestinians and the other for Israelis, as a pivotal step toward a conclusive resolution to the prolonged and costly conflict. Unfortunately, the intended implementation of these agreements faltered, resulting in failed efforts and the division of Palestinian society between Fatah in the West Bank and Hamas in the Gaza Strip. Instead of fostering confidence, Israeli positions hardened toward Palestinians, leading to a surge in settlements in the West Bank and east Jerusalem. Currently, approximately 700,000 Israelis reside on lands designated for the Palestinian State, contributing to a decline in both regional and global interest in the matter.
The Palestinian cause regained global prominence with the events of October 7, marking the end of a three-decade stagnation and a background role amid the Arab Spring and subsequent regional and global crises. The Israel-Hamas War raised international concerns about the potential escalation into a regional war. It heightened fears of derailing the Middle East peace process, particularly the "two-state solution." Israeli officials have recently declared that this option no longer exists, despite opposition and warnings from some of Tel Aviv's closest allies, notably Washington.
These indicators underscore the notion that stability in the Middle East hinges on a resolution to the Palestinian cause that aligns with the national aspirations of the Palestinian people. Consequently, discussions surrounding a two-state solution have resurfaced as the optimal proposal to end the conflict, serving as an alternative to the right-wing expansion and settlement policy on the West Bank. Such a policy could potentially isolate and compromise Israel's security while significantly depleting its military and financial resources. Hence, this analysis addresses the crucial question: Is the two-state solution still viable given the current circumstances?
30 Jan 2024
The Vicious Cycle of Violence: Next Steps Post-Jordan Attack
On Jan. 28, 2024, a significant drone strike occurred at an American military outpost situated along the Jordanian-Syrian border. The targeted attack led to the death of three American troops, with 34 additional personnel sustaining injuries, as reported in the latest statement released on Jan. 30, 2024.
This event holds profound implications and is poised to instigate repercussions that warrant careful analysis and monitoring. Notably, it marks the first instance of American service members being killed by hostile fire in the Middle East since the commencement of the Israel-Hamas War. The attack's location and timing carry additional connotations, underscoring the need to anticipate and evaluate the potential developments that may occur.
Moreover, the Islamic Resistance in Iraq (IRI) claimed responsibility for the attack in a statement, explicitly stating, “We targeted four enemy bases, including three situated in Syria: Al-Shaddadi base, Al-Rukban base, and Al-Tanf base (located near the Syrian-Jordanian border). The fourth targeted base is within the occupied Palestinian territories, identified as the Zevulun Naval Facility.”
11 Jan 2024
Israel and the ICJ: Resuscitating Global Order
South Africa’s case against Israel at the ICJ is a welcome attempt to revive the global social order but failure to bring about real proportionate justice will only further confirm the current state of international anarchy and embolden other rogue actors.
On Jan. 11, 2024, Israel appeared before the International Court of Justice in The Hague at the first hearing in the case presented against it by South Africa. Israel has been accused of committing the crime of genocide and may be subjected to provisional measures, which would request it to decrease all acts from within Article II of the Genocide Convention and halt its military operations in the Gaza Strip. The State of Israel, established in 1948, the same year that the U.N. Genocide Convention was adopted, may be charged with breaching the Convention, of which it is a signatory.
18 Oct 2023
Hannibal Protocol: Will Israel Burn Hamas’s Leverage?
The emergency government of Israel has taken decisive steps, announcing its intent to declare war and initiate comprehensive ground invasion preparations in response to the recent incursion by Palestinian factions on October 7, 2023. This incursion targeted over 20 locations surrounding the Gaza envelope. It resulted in the capture of numerous Israeli soldiers and officers stationed along the front lines in the Gaza Strip's secure zones. The present prisoner crisis is one of the most severe episodes in the long history of confrontations between Israel and Palestinian factions.
11 Apr 2023
Between Grain and AK-47s: Russian Influence in Africa
The Russian presence in Africa has recently increased after a decline of nearly three decades since the dissolution of the Soviet Union in the nineties of the last century. Russian-African relations are part of Russia's new strategy to enhance its international influence. This strategy conforms to Russia's situation in international affairs, including its support for countries that contradict Western policies. Moscow has focused its influence on the West African region, taking advantage of Western policy mistakes, the mounting anti-European sentiment, and the long-standing failure of international and domestic actors to address the root causes of the regional instability. The first Russian-African summit in Sochi in October 2019 concluded contracts with more than 30 African countries for the supply of weapons and military equipment. It thus opened the door for state-backed companies to invest heavily in the security and technology sectors and industries that extract natural resources such as oil, gas, gold and other minerals.
On the other hand, the Russian-Ukrainian conflict did not impede this rapprochement but rather contributed to developing the partnership between the two parties to take the form of a strategic alliance. This was apparent in the speeches and statements of President Vladimir Putin, the most prominent of which was the speech he delivered at the International Parliament Conference "Russia - Africa in a Multipolar World", which was held in Moscow in March of this year on the sidelines of Saint Petersburg preparations for the second coming Russian – African summit to be held in July 2023. Putin reiterated that cooperation between Moscow and African countries was and will always be one of the top fixed priorities of Russia's foreign policy, declaring Russia's fulfilment of all its obligations, including supply of food, fertilisers, fuel and other essential products to the countries of the continent, which helps ensure food and energy security.
In light of the ongoing Russian-Ukrainian conflict, this analysis aims to shed more light on the motivations and characteristics of the Russian strategy in Africa. It also seeks to highlight the challenges to Russian influence expansion as well as the prospects for Russian-African relations in the future.
4 Apr 2023
Is Islamophobia on the Decline in Europe?
Islamophobia is a combination of hatred, fear, and prejudice towards Islam and Muslims. This phenomenon is manifested in violence against Muslims and Islamic symbols, as well as discrimination and antagonism in daily life. Over the last two decades, there has been a sharp rise in anti-Muslim prejudice, leading many nations to take unjustified action against Muslims in response to the security concerns that have been levelled against them. The persistence of prejudice and hatred against Muslims is also a result of widespread misconceptions about Islam. In addition to several incidences targeting Muslims and their symbols, Islamophobia has spread through statements, attitudes, and campaigns that fuel anti-Muslim sentiment. Muslims frequently face discrimination in countries where they are a minority and have trouble accessing products and services, education, and jobs. Islamophobic hate crimes typically rise following particular occurrences, such as terrorist acts, often provoking collective punishment.
On the other hand, there has also been an increase in tolerance recently, with a noticeable expansion of Muslim celebrations and rituals in various European cities. For example, Ramadan was observed in London by a few English clubs and Muslim footballers were given time to break their fast by English Football Association. The German Federal Ministry of Education and Research also issued a letter allowing Muslim instructors in Berlin to wear the veil (hijab). Considering these seemingly minor but significant societal developments, this analysis investigates the repercussions of these changes on the presence of Islamophobia in Europe to determine whether the phenomenon has declined or if these manifestations are still too superficial to affect the depth and roots of the issue.
30 Mar 2023
Netanyahu’s Judicial Amendments and the Future of the Palestinian Cause
In recent months, protests inside Israel have increased significantly in response to Israeli Minister of Justice Yariv Levin's announcement of the judicial overhaul plan on January 4, 2023. Protests have been held every week since Yariv's announcement. On February 12, 2023, Israeli President Isaac Herzog delivered an unusual address in which he warned of the consequences of this plan and its harm to Israeli society, economy, and security. The president attempted to mediate a reconciliation between the opposition and the ruling coalition, but he was unsuccessful. Nevertheless, the coalition began its strategy; on March 20, 2023, the Knesset passed the first reading of the proposal regarding the eligibility of ministers and deputy ministers with a majority of 63 members. In addition, the proposal states that courts, including the Supreme Court, are not allowed directly or indirectly to hear cases relating to the appointment or dismissal of ministers from office. This proposal is one of the most crucial components of the judicial amendments plan.
29 Mar 2023
Sports Diplomacy: How Do Sports Events Enhance the Reputation of Countries?
The FIFA World Cup in 2022 in Qatar garnered more attention from the international community due to Qatar's ability to change perceptions of it as a nation capable of hosting the biggest sporting events. Many countries have recently sought to host international sports events in an effort to enhance their posture diplomatically, improve their reputation as well as shore up their position within the international community. To that end, “Sports Diplomacy” has been used to achieve understanding and peace among nations and promote the countries’ political and ideological goals. On the other hand, countries exploited sports as an approach aiming at asserting the superiority and strength of the state; for instance, the 1936 Olympic Games were held in Germany, and the 1934 FIFA World Cup was held in Mussolini’s Italy. In other cases, sports played a more constructive role in the 1990s, representing an opportunity for South Africa to surpass the apartheid era and look forward to a better future. For China, sports have played a role in introducing an open policy and a more influential economy.
A state’s reputation is one of the key factors affecting its international relations, as it reflects its global image, influencing its recognition and interaction with other countries. With sports diplomacy, states could carry out several interests, such as boosting diplomatic ties with other states, raising the degree of understanding and cooperation among people and governments, and improving the state's public image globally. In other words, sports diplomacy is an effective tool for attaining diplomatic goals and promoting the state’s reputation worldwide. This analysis seeks to shed more light on the link between sports diplomacy and the state’s reputation and how the state’s stance in the international community is enhanced by sports diplomacy.
23 Mar 2023
A Window of Opportunity: A Reading of Turkey’s Position on Sweden and Finland’s NATO Membership
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) philosophy is based on promoting peace and stability and protecting the security of its members through a European and North American defence alliance. The alliance enjoys an "open door policy" whereby any European country willing to undertake the obligations and commitments of membership is welcome to apply for membership. Any decisions on expansion must be approved by a unanimous vote of the current 30 members. The essential feature of the alliance is Article 5 of the Washington Treaty on Collective Defence, which establishes NATO as a powerful alliance that guarantees security by the military response and protects any member state if it is attacked.
5 Feb 2023
Double Standards: Signs of Denying Lebanon the Right to Vote in the UN
The recent statement by UN Secretary-General António Guterres on January 17, 2023, that Lebanon and eight other countries will lose their right to vote in the UN sparked various concerns about the standards used to make this decision. Looking at the disenfranchised list, we find common problems in these countries. Some countries—like Somalia, South Sudan, and Lebanon—suffer from political and economic crises, while others—like Venezuela—suffer from economic sanctions that have wreaked havoc on their economies. Such a decision highlights how crucial it is to link democracy with justice and raises whether the countries’ rights depend on their financial resources. Is it unacceptable for underdeveloped and distressed countries to participate in international forums and voice their thoughts? Some other countries violated, and continue to break, International Law and the UN Charter; however, they enjoy their voting rights. In addition, the UN is the primary international platform where countries seek to resolve their differences without resorting to conflict. Countries have to participate in this entity to make their voices heard in the global community; if they are excluded, they will assume individual responsibility for forging solid alliances and searching for alternative sources of communication with the rest of the worldwide community.
The current analysis aims to evaluate the provisions and procedures on which the nine countries were denied the right to vote to determine the key drivers of the decision and how the nine denied countries may restore their voting rights.
12 Jan 2023
The Future of Youth in the Post-Oil Era: The Case of the United Arab Emirates and Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
One of the most critical issues currently facing the Middle East is the changing composition of its demographic structure. A massive cohort of young people — known as a youth bulge — is challenging policymakers, with youth policies affecting security, education, the labour market, and welfare programs, among other areas. Given the relative stability and wealth of the Gulf states, this is an issue that is not often associated with the region. However, handling a growing young population is just as challenging in the Gulf.
The Gulf is one of the wealthiest regions worldwide; in terms of GDP per capita, it is distinctive due to its unique hydrocarbon reserves compared to a relatively small national population. Gulf states rely on oil revenue — to varying degrees — to attract private investors and provide extensive public services and subsidies to nationals. With not enough diversification in their economies, government spending in the Gulf states will continue to be a barrier to economic diversification. To sustain the high standard of living attained by Emirati and Saudi societies to the youth and the coming generations, the two countries must set strategies and plans to integrate youth while continuing to diversify their economies away from oil. This study explores the impact of the post-oil reforms and strategy on the youth, including education, employment, social contract, and identity.
The study applies Late Rentier State Theory to analyse the relationship between youth, the Emirati and Saudi states, the post-oil reforms, and their future trajectories. The analysis is guided by some of the characteristics identified by Late RST which focus on the impact of globalization, modernization policies, diversification, the state’s encouragement of entrepreneurship, and the sustainability of their strategies with regards to the extent to which they accommodate youth’s needs and account for changing societal structures and expectations.
While the study does not refute the youth bulge hypothesis, which contends that states where young adults constitute a large proportion of the population are expected to face an elevated risk of political violence and interstate conflict, widely used in the literature; it adds to it by proposing that while those risks exist, they can be alleviated under certain circumstances. Those circumstances include policies and strategies to be taken by governments that are relevant to youth needs and the surrounding environment. Namely, taking into consideration both agency and structure.
The study finds that, for the United Arab Emirates, the results of education and Emiratisation policies are likely to shape the shifting social contract between young Emiratis and the government, and could lead to a range of outcomes, from the promising- a population of empowered, educated, and skilled Emirati youth- to the stagnant- disappointed and apathetic youth persistent in their preference of the public sector- to the more worrisome- yet unlikely- active opposition by dissatisfied youth.
With regards to the Kingdom Saudi Arabia, the study finds that while the government is investing massively in educational and employment reforms, young Saudis need to adopt entrepreneurial values and work ethic to ensure the success of “Neo-Saudism". This in turn requires a certain level of responsiveness from the government and possibly more opportunities for youth to participate in decision making in the near future. The speed of change and the extent to which youth’s values and perspectives may clash with those of older generations is yet to be determined. The real challenge for Saudi decision makers and strategists will be in maintaining balance and stable relations between different societal groups.
22 Dec 2022
Securing the Future Generation: A Road Map for Arab Nuclear Cooperation
Nuclear cooperation attracts international and regional attention, many Arab countries have aspired to produce clean nuclear energy and have either begun or are seeking to join the nuclear energy club. The United Arab Emirates (UAE), The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) , Egypt, and Jordan, are the frontrunners in the Middle East and therefore will be the focus of this paper. Nuclear power is an international industry in terms of operation, supply chains, and vendors, as well as nuclear safety, non-proliferation and waste management, therefore, there is an ongoing need for cooperation and collaboration between states. This cooperation can include sharing technical expertise and nuclear technology, establishing agreements that facilitate nuclear exports, agreements on nuclear safety and standards, and collaboration with regulatory frameworks.
The paper employs horizontal or environmental scanning to analyse the current position of nuclear energy in each country and their preparedness for nuclear cooperation, as well as existing models of nuclear cooperation in other regions. Thereafter, the paper explores the different incentives countries may have for engaging in nuclear cooperation, including the potential benefits to be gained. A SWOT analysis is used to structure the environmental scanning, evaluating the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats within each country with regards to their potential role and contribution to nuclear cooperation in addition to an overall SWOT analysis of the countries as a whole with regards to the prospect of ongoing collaboration.
The paper is divided into three chapters; the first chapter provides an overview of nuclear energy in each of the selected countries, the second chapter examines existing models of nuclear cooperation and analyses the different enabling factors which will later be used to identify opportunities for Arab nuclear collaboration, and the third chapter analyses the various economic, political, and security incentives that would drive countries to seek cooperation or that can be used to advocate for greater collaboration among policymakers.
A cooperation model is produced as a result of this analysis, highlighting key characteristics of the ideal regional partnership. Three scenarios for Arab nuclear cooperation are evaluated to demonstrate what could occur if this proposed cooperation occurs, how it would happen, and the scenarios of no collaboration or limited cooperation.