Dr. Mohamed Shadi has a PhD in Economics and Public Finance and a master’s degree in International Law. He is a teacher of Political Economy at the National Training Academy (NTA) of the Presidency of the Arab Republic of Egypt, a teacher of Transport and Energy Economics at the Arab Academy for Science, Technology, and Maritime Transport (AAST) of the Arab League, a political economy expert at the Egyptian Centre for Strategic Studies (ECSS), and a columnist for several Egyptian newspapers.
He has ten years of expertise in political economy and energy economics and has undertaken several studies in both and has provided decision-makers with several policy papers and alternatives.
contact information
Latest By Dr. Mohamed Shadi
23 Jun 2025
Containment to Confrontation: U.S. Intervention in Iran
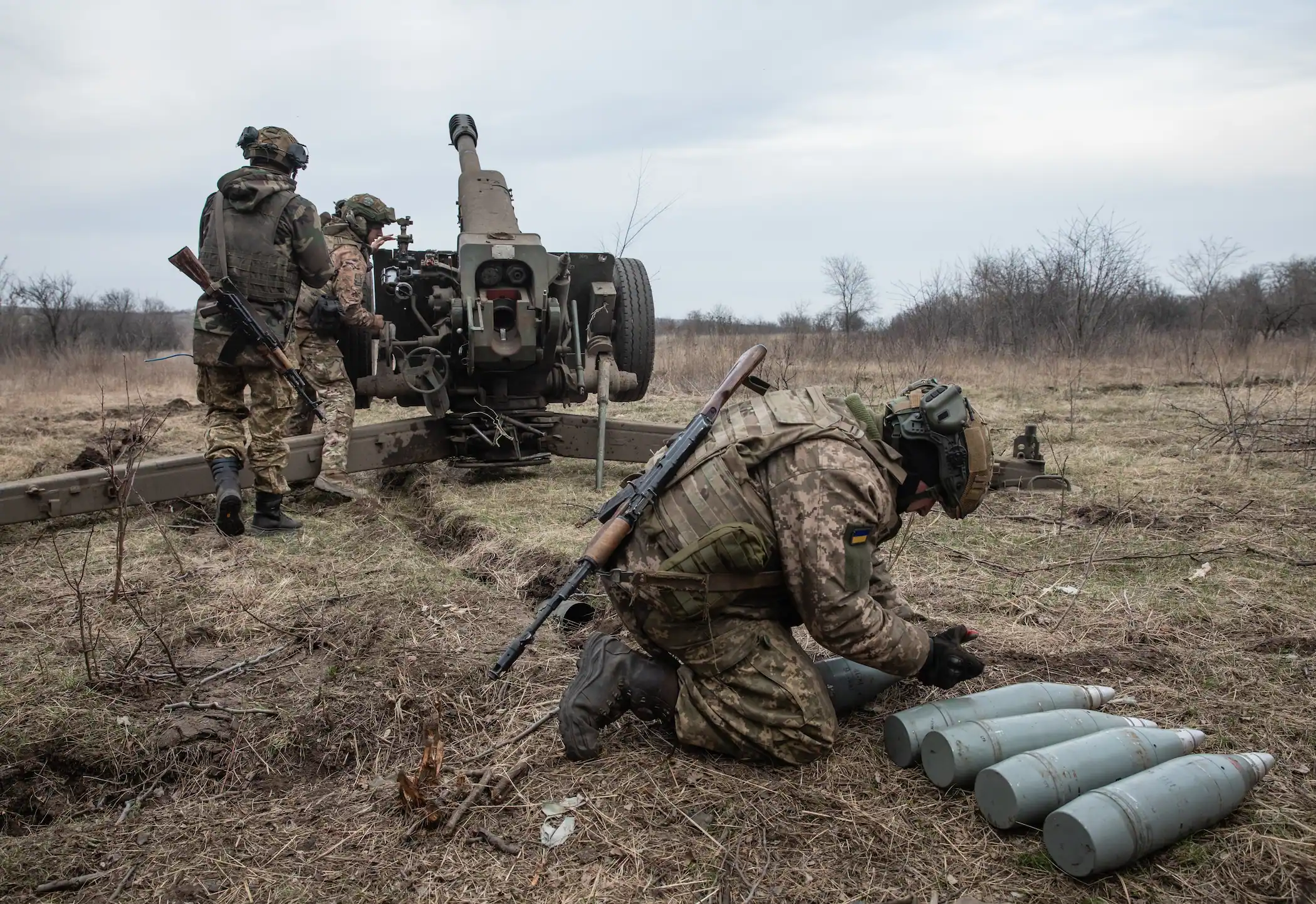
In the early hours of June 22, 2025, the Middle East entered a new phase of strategic confrontation following the United States' execution of a calibrated series of precision airstrikes against three of Iran’s most critical nuclear facilities: the Fordow Fuel Enrichment Plant, the Natanz Enrichment Complex, and the Isfahan Nuclear Technology Center. These strikes marked a significant inflection point in American policy toward Iran's nuclear program, signifying a deliberate departure from the long-preferred instruments of sanctions, diplomacy, and covert sabotage toward direct military action aimed at functionally dismantling Iran’s enrichment capacity.
The U.S. intervention did not occur in a vacuum but was preceded by a sweeping nine-day Israeli air campaign— “Operation Rising Lion”—which inflicted substantial damage on Iran’s conventional military and nuclear infrastructure. Yet U.S. strategic assessments concluded that Israeli capabilities alone would fall short of neutralizing the deeply buried Fordow facility, located nearly 90 meters beneath the mountains near Qom. Accordingly, Washington deployed B-2 Spirit bombers from Whiteman Air Force Base and launched submarine-based Tomahawk cruise missiles, employing—for the first time in combat—the GBU-57 Massive Ordnance Penetrator, a 30,000-pound precision-guided “bunker buster” weapon. The strikes were designed not merely to degrade but to decapitate Iran’s uranium enrichment trajectory at every critical juncture.
While the U.S. administration proclaimed the operation a “complete and total success,” Iran’s leadership sought to downplay the extent of the damage, signalling both resilience and continued intent to pursue its nuclear ambitions. Tehran’s initial response refrained from large-scale direct retaliation, instead signalling a likely pivot toward asymmetric reprisal via regional proxies such as the Houthis, alongside diplomatic escalation and renewed threats to abandon the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT). This calibrated restraint highlights the regime’s acute awareness of the potentially existential consequences of a direct confrontation with the United States.
Structurally, the strikes reflect a paradigmatic shift in U.S. non-proliferation doctrine: from risk management through deterrence and arms control to selective, high-precision coercion. The operation also underscores a changing regional deterrence architecture, in which American military intervention is no longer conditioned by alliance consensus or Gulf coordination, as several key Arab states were reportedly excluded from prior notification. This signals an American willingness to act unilaterally—or bilaterally with Israel—when core proliferation red lines are deemed to have been crossed.
22 Jun 2025
What If: Iran Attacked the Dimona Reactor?
Amid the intensifying confrontation between Iran and Israel throughout 2025, the prospect of a direct strike against Israel’s Dimona nuclear facility has moved from a remote possibility to a plausible escalation scenario. As military operations increasingly target strategic infrastructure on both sides, the regional system faces the risk of a threshold breach—one that could trigger not only military and political consequences but also a multidimensional crisis involving radioactive contamination, mass displacement, and economic collapse across multiple states.
While Israel would undoubtedly bear the immediate brunt—facing mass civilian evacuations, irreversible environmental degradation in the Negev, and the paralysis of its agricultural and tourism sectors—the ripple effects would extend far beyond its borders.
Jordan’s border regions and agricultural zones in the Jordan Valley could face contamination and humanitarian strain, potentially requiring the evacuation of tens of thousands of people. Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula and northern Suez region could suffer fallout exposure, disrupting global shipping through the canal and threatening the Red Sea tourism corridor. Saudi Arabia’s northern provinces, including areas tied to its Vision 2030 megaprojects, could face both environmental and demographic disruption.
15 Jun 2025
The Erosion of Iranian Deterrence
Between June 13 and 14, 2025, Israel executed one of the most daring and sophisticated military operations in its contemporary history: a multi-pronged aerial strike that penetrated deep into Iranian sovereign territory in an unprecedented fashion. The offensive targeted critical nuclear infrastructure, including the Natanz and Fordow enrichment facilities, alongside additional military installations near Isfahan. Furthermore, the operation struck key airbases integral to Iran’s air defence network, most notably Hamadan and Tabriz airfields. In parallel, Israeli forces targeted senior leadership within both the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) and the conventional military, with subsequent intelligence assessments confirming direct hits and casualties among Iran’s high command.
Iran's response, though swift, bore the hallmarks of operational improvisation. Seeking to reassert deterrence and project resilience, Tehran launched over one hundred unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) on the same day, primarily of the Shahed-136 and Shahed-131 variants. These drones traversed approximately 2,000 kilometres through Iraqi and Syrian airspace. However, the majority failed to reach Israeli territory. Instead, they were intercepted by a multi-layered defensive network composed of Jordanian, Saudi, and Israeli air defence systems, all heavily supported by U.S. early-warning and tracking technologies. A large number were neutralized over Iraq’s Anbar province and the deserts of Jordan, while others were downed over northern Saudi Arabia.
On June 14, Iran escalated by launching its principal retaliatory strike in the form of a large-scale, coordinated ballistic missile attack. Over 150 ballistic missiles were deployed, prominently including Ghadr-110 (with a range of up to 3,000 km), Khorramshahr, and Sejjil-2—among the most advanced systems in Iran’s medium-range missile arsenal. These missiles targeted multiple sites deep inside Israeli territory. A notable strike occurred near Israel’s Ministry of Defence compound in the Kirya complex in central Tel Aviv, where one missile reportedly caused structural damage and minor injuries, though no fatalities among military personnel were confirmed. Additional missiles struck civilian infrastructure in Tel Aviv, Ramat Gan, and Rishon LeZion, injuring several individuals—one critically—with the majority suffering only mild to moderate wounds.
Despite the magnitude of the missile barrage, the strategic yield fell significantly short of Tehran’s expectations. This underperformance prompted Iranian authorities to broaden the scope of their confrontation, issuing explicit warnings that U.S. military assets across the region—particularly in the Gulf—would henceforth be considered legitimate targets. These threats referenced high-value installations such as Al Udeid Air Base in Qatar, Al Dhafra Air Base in the United Arab Emirates, and U.S. military positions in Iraq, including Ain al-Asad and Camp Victoria in Baghdad, as well as naval facilities in Bahrain.
From Iran’s strategic vantage point, any U.S. involvement—especially in reinforcing Israeli air defences—constitutes direct participation in the hostilities. This rationale is now used to justify Tehran’s threats to strike American military positions across the Gulf. The implications of this shift are profound: for the first time since 2020, the prospect of open military confrontation in the Persian Gulf has become a credible geopolitical scenario. The regional deterrence equation, long balanced on latent threat and calculated ambiguity, has now entered a phase of dangerous volatility.
This analysis seeks to offer a comprehensive examination of the strategic motivations underpinning Iran’s threats to target U.S. military bases in the Gulf region. By synthesizing operational data—namely, Iran’s patterns of ballistic missile and drone deployment—with broader structural dynamics of regional and international power distribution, to elucidate the strategic logic through which American military installations in the Gulf emerge as priority targets within Iran’s evolving deterrence doctrine.
14 Jun 2025
Strategic Assessment: The “Rising Lion” Strike and the Reshaping of Regional Security in the Middle East
On June 13, 2025, Israel launched an unprecedented and overt military operation against Iran, codenamed "Operation Rising Lion", marking a decisive shift in its strategic doctrine regarding Tehran’s nuclear trajectory. The operation, involving more than 200 combat aircraft—including F-15Is, F-16Is, and F-35s—targeted key nuclear infrastructure, foremost among them the Natanz enrichment facility, in addition to sensitive military and intelligence compounds in Tehran and suspected subterranean missile installations across multiple provinces.
The aerial strikes were not executed in isolation. They were accompanied by limited ground incursions carried out by Israeli special operations forces inside Iranian territory, alongside locally launched drones and sabotage missions activated by embedded networks, indicating a hybrid warfare architecture integrating airpower, cyber capability, and covert assets.
The operation resulted in the assassination of several senior Iranian military officials, including IRGC Commander Hossein Salami and Armed Forces Chief of Staff Mohammad Bagheri, as well as prominent nuclear scientists. Nevertheless, the intensely fortified Fordow enrichment facility, situated beneath a mountain near Qom, remained untouched, preserving Iran’s technical capacity to resume high-grade uranium enrichment if it chooses to do so.
Iran’s immediate response consisted of launching over 100 armed drones toward Israeli airspace, followed by announcements to construct a new, “impenetrable” enrichment site and to upgrade centrifuge infrastructure at Fordow. Globally, oil prices surged by over 10% within 24 hours, reflecting fears of regional destabilisation, particularly in light of Iran’s proximity to critical maritime chokepoints.
This paper thus aims to analyse the likely contours of Iran’s retaliatory strategy and to assess the broader geopolitical ramifications of the Israeli strike, particularly as they pertain to the security and strategic postures of the Arab Gulf in light of the retaliatory actions of Iran.
30 Apr 2025
The 2025 European Blackout: Grid Fragility, Renewables, and Lessons for the Middle East
On April 28 2025, Europe experienced one of its most disruptive technological collapses in modern history. A sudden, cascading failure of the power grid cut off electricity all over Spain, Portugal, parts of France, Germany, and Italy, immobilising vital infrastructure such metro systems, airports, hospitals, and telecommunications. Spain alone suffered an unmatched 15 GW loss in five seconds, reducing roughly 60% of its power need. Emergency states were declared; recovery, albeit quick in some areas, revealed systematic weaknesses in the European energy framework that resonate far outside the continent.
18 Dec 2024
Mahabad: Oil, the Peshmerga, and the Collapse of the Kurdish Dream
The Kurdish dream of establishing an independent state was on the verge of realisation after centuries of demands in Jan. 1946. This came when “Qazi Mohammad,” the Iranian Kurdish leader, declared the establishment of the Mahabad Republic in the province of the same name, now part of the Islamic Republic of Iran. However, this dream quickly dissipated when the Soviet Union withdrew its financial support for the nascent state. The intensification of the economic blockade on the region further compounded the situation, preventing the entry of food supplies and reducing agricultural production. These pressures led to dramatic shifts in the loyalties of Kurdish tribal leaders who had initially allied with “Qazi” during the state's formation, hoping to secure a share of Soviet financial and food aid.
The food situation worsened over time, pushing some leaders of the Mahabad army to leave the capital, especially as Iranian forces were nearing its entrance, leaving the Kurdish leader and a small Kurdish group behind to face an unequal battle with the Iranian army. Therefore, to spare Kurdish blood, it was decided to surrender on December 15 of the same year, leading to the Iranian army's occupation of Mahabad and the declaration of the state's fall. In the end, “Qazi” was executed in March 1947, marking the end of the closest attempt to establish a Kurdish state.
About a quarter of a century later, the Iraqi Federal Supreme Court issued a series of rulings regarding Iraqi oil exported by the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. The latest ruling, issued in Feb. 2024, mandated the Kurdistan Regional Government’s Council of Ministers to hand over all oil and non-oil revenues to the central government in Baghdad. This could have a dual impact similar to that caused by the cessation of financial support and the Iranian blockade on the Mahabad army, but this time it affects the Peshmerga forces that represent the hope for preserving the “autonomy” of the Kurdistan Region of Iraq considered the second closest Kurdish attempt at establishing a national homeland for the Kurds.
Therefore, the First Part of this paper addresses the political situation of the Kurds, focusing on the status of the region in the Iraqi Constitution, the contentious issues between the region and the federal government, and the impact of these disputes on the continuity and existence of the Peshmerga. The Second Part reviews the economic situation, examining the effects of the series of judicial rulings on the conditions that undermine the autonomy of the regional government in selling oil and the repercussions of this on the Peshmerga as a Kurdish defence force that protects the “autonomy” of the region, forming the last line of defence against its collapse.
5 Nov 2024
Political Financing: Motivations and Barriers in the Race to the White House
Winning a U.S. presidential election hinges on a complex interplay of factors, among which campaign strategies, candidate credentials, media influence, public accessibility, socioeconomic contexts, and voter sentiment are key. Yet, the fundraising and resource allocation process is central to these dynamics—the driving force that propels these elements toward a more significant impact. Fundraising serves as both the lifeblood of the campaign machinery and a catalyst for enhancing the effectiveness of other campaign components. Consequently, extensive research has studied the correlation between financial backing in U.S. presidential campaigns and candidates' success. Although findings vary widely, a consensus has emerged around the essential role of funding in mounting a viable campaign. Divergences among studies, however, suggest that the sheer volume of funds raised does not consistently predict electoral success. This nuance became particularly evident in the 2016 and 2020 presidential campaigns, where the connection between campaign financing and the likelihood of victory appeared less direct, signalling a shift in campaign financing dynamics and evolving voter priorities.
On the other hand, the scale and nature of campaign funding reveal insights into voters’ preliminary preferences, political leanings, and a potential president's anticipated priorities and agenda. Campaign funding reflects the candidate's backing base and hints at the strategic tools and priorities the next administration might emphasise. This analysis thus examines the funding sources behind the Democratic and Republican presidential campaigns—the largest and most competitive contenders for the White House.
6 Oct 2024
A Year of War: Netanyahu Claims Victory, Israel Experiences Defeat
A whole year has passed since Hamas' military operations in the Gaza Strip Envelope, marking what many considered the first Palestinian incursion into Israeli territory since the war that led to Israel’s establishment in the late 1940s. The war resulted in the capture of dozens of Israelis and the deaths of hundreds more. In response, Israel launched its most extensive military campaign since the 1973 Sixth of October War, aiming to rebuild its fragmented deterrence capabilities and restore its diminished regional stature. This effort involved tens of thousands of airstrikes and the monthly deployment of approximately 10,000 artillery shells. Over 66% of the buildings in Gaza were damaged, with about 163,700 structures affected, including the complete destruction of 52,500 buildings. The human cost was equally staggering, with over 41,000 Palestinian fatalities recorded. The situation remains unresolved, leaving the war's toll ongoing. The destruction has not been confined to Gaza alone. The financial and reputational costs for Israel have been severe. Though the thousands of missile attacks launched by Hamas had limited impact on Israel's critical infrastructure, they significantly undermined its economy and tarnished its image as a secure, advanced economy. This prompts a thorough analysis of the war's impact on Israel's economic stability over the past year and a projection of its potential long-term consequences.
18 Sep 2024
Restoring Lost Deterrence: Pager Explosions in Lebanon
In a well-coordinated assault targeting Lebanon’s southern suburbs—an area known for being a Hezbollah stronghold—and specific regions in Syria, hundreds of pager devices used by Lebanese Hezbollah members were detonated simultaneously. Early reports, at the time of writing, suggest the attack claimed the lives of over a dozen individuals and left thousands more injured.
Israel has a long-established record of carrying out extrajudicial operations, ranging from targeted assassinations to sophisticated cyber-attacks aimed at its adversaries. A hallmark of its tactics includes booby-trapping communications devices, as seen in the 1996 assassination of Yahya Ayyash, a prominent Hamas bomb maker, who was killed using a bomb concealed within his mobile phone. Given this precedent, it is plausible that Israeli intelligence, specifically the Mossad, orchestrated the recent operation by infiltrating the manufacturing process of these pager devices, possibly embedding lithium-ion batteries rigged with meticulously calibrated explosives.
The operation raises many questions about the strength of the security of Hezbollah’s communications infrastructure, which calls for looking at the incident from a deeper perspective to decipher its meanings and implications from the perspective of the communications security used by Hezbollah or other resistance groups in the region or even regular armies in the Middle East.
8 Sep 2024
Monetary Policy Shockwaves: Unrest Across Africa Amid Tightening Measures
The global economy operates under cyclical phases of monetary tightening and easing, often contrary to the business cycle. In periods when business activity reaches its lowest ebb and teeters on the edge of recession, expansionary monetary policy is implemented to redirect this downward trajectory, averting a slide into economic contraction. This approach prevents the economy from experiencing a sudden surge in growth, which could push it toward unsustainable heights. Conversely, contractionary monetary policy is deployed to rein in unchecked growth, preventing it from spiralling into inflationary pressures that could erode economic progress and deplete citizens' savings. By tempering both extremes, monetary policy strives to maintain a stable path of moderate growth that ensures long-term national economic health without tipping into volatility or stagnation.
Monetary policy tools tend to operate similarly across global economies, with one critical exception: the influence of the U.S. Federal Reserve. The Fed’s actions transcend the U.S. market, shaping global financial conditions. For instance, a decision to hike interest rates in the United States has far-reaching effects on consumer spending globally, even if these impacts manifest indirectly. This global ripple is acutely felt in African nations, where populations are particularly vulnerable to the consequences of U.S. monetary tightening, notably during interest rate hikes. This analysis, therefore, seeks to explore the relationship between the Federal Reserve’s tightening of monetary policy over the past three years and the subsequent waves of instability that have spread across the African continent. These effects continue to play out at the time of writing, despite recent signals that the Fed may shift once again toward a more expansionary stance.
3 Sep 2024
Will Germany’s Political Shift Alter Europe’s Stance on Ukraine?
The recent local elections in the German states of Saxony and Thuringia signal a significant extension of the influence of extremist movements, particularly far-right factions, across the European political landscape. This development underscores the resurgence of nationalism, challenging the liberal trends that have dominated the continent since the fall of the Berlin Wall and the end of the Cold War. If replicated across other regions, the election outcomes in these two states could have profound repercussions for Germany’s political and economic future, especially for the ruling coalition led by Chancellor Olaf Scholz. The key results and their potential implications are outlined below:
29 Aug 2024
The Core Issue: Ammunition Manufacturing and its Effects on the Russia-Ukraine War
The Russia-Ukraine war has now entered its 18th month, with neither side achieving decisive strategic or operational control, bringing the conflict closer to a protracted stalemate rather than a resolution at the negotiation table. This prolonged uncertainty suggests that the war may continue for several more months before either party considers a truce. A similar situation is unfolding in Gaza, where the war is now in its ninth month, making it one of the longest wars in the history of the Arab-Israeli conflict, rivalled only by the wars surrounding the establishment of Israel and the War of Attrition with Egypt. Here, too, there is little indication that a resolution or even a willingness to negotiate a truce is forthcoming from either side. The possibility of a decade marked by extended wars looms on the horizon, especially if a conflict were to break out between China and one of its neighbours, whether in the Taiwan Strait or the South China Sea. This scenario is increasingly plausible given the United States' (U.S.) involvement in regional and international political and economic skirmishes directly targeting Chinese interests.
The current and anticipated wars share two key characteristics, in addition to the fact that they have taken or may take longer to resolve than expected. Firstly, they are occurring or expected to occur in regions of immense strategic importance to the world, such as the Great European Plain—one of the world's most fertile areas and a major grain-producing region—or in the heart of the Middle East, a critical juncture for global trade and energy routes. Secondly, these wars are not merely between individual countries or parties but involve broader alliances. For instance, in the Russia-Ukraine War, North Korea and Iran are indirectly aligned with Russia, while NATO supports Ukraine. Similarly, in the Israel-Hamas War, the U.S., Britain, and France are aligned with Israel, whereas Iran, Hezbollah, the Houthis, and numerous Shiite militias in Iraq and Syria support Hamas.
These two characteristics have imparted the ongoing wars with traits that, to some extent, echo those of the First and Second World Wars, particularly in terms of the intense consumption of ammunition and the resulting high death rates among the warring parties, as well as the extended length of the engagement lines. As a result, both wars have begun to consume vast quantities of ammunition and conventional weapons, especially artillery shells, to the point where the stockpiles of the forces involved have been significantly depleted or are nearing exhaustion. This depletion has made the replenishment of supplies inevitable, transferring the pressure of the battlefield to the production lines in factories. However, these factories have frequently struggled to meet the front lines' demands or replenish stockpiles, leading to a severe shortage of ammunition on all fronts for all parties involved.
This scarcity has transformed the war into a series of industrial battles, where the side with greater industrial capacity gains the upper hand by supplying its forces with more ammunition, thereby securing a tactical advantage. As a result, industry has become a direct and critical component of national security in its most narrow sense. Consequently, this analysis examines the impact of industrial capacity on the Russia-Ukraine war, focusing specifically on the artillery capabilities of both sides.
25 Aug 2024
The Economic Ramifications of Israel’s Pre-emptive Strikes on Hezbollah
In the morning of Sunday, Aug. 25, the Israeli army carried out a pre-emptive strike, launching intensive air raids with around 100 fighter jets targeting over 40 sites believed to be Hezbollah’s precision missile launch points. These sites were allegedly being prepared for strikes against Israel’s northern border in retaliation for last month’s assassination of Hezbollah’s military commander, Fouad Shukr. In response, Hezbollah launched a significant counterattack later in the morning, deploying numerous drones and firing over 320 Katyusha rockets at Israel, hitting 11 military targets. The escalation raises concerns, particularly as the Israeli government plans to allow residents to return to the northern areas they evacuated nine months ago. Should Israel fail to mitigate Hezbollah's ongoing strikes, the situation could have severe political and security repercussions for the government. This analysis examines the immediate and direct economic impacts of these mutual attacks on both sides of the border, and the potential broader consequences should the war continue and intensify.
22 Aug 2024
Recurring Patterns: How Will Iran Respond to Ismail Haniyeh’s Assassination?
The world has been on edge since July 31,2024, awaiting Iran’s response to the assassination of Ismail Haniyeh, head of the Hamas political bureau, in Tehran by an Israeli attack. Haniyeh was targeted while attending the inauguration ceremony of Iranian President Masoud Pezekshian, marking a direct challenge to Iranian sovereignty and its role as a regional leader of resistance movements. This event underscores the broader confrontation between Iran, which opposes what it perceives as the United States and Israeli dominance in the region. Given the assassination's symbolic and strategic significance, many see Iran’s retaliation as inevitable, particularly amid escalations between Israel and Iran. Notably, this incident is part of a broader series of high-profile killings targeting figures within the so-called resistance axis. Just hours before the explosion in Tehran, Israel launched a missile strike in Beirut's southern suburbs, killing Fouad Shukr, a senior Hezbollah military official, while also claiming—without confirmation—the assassination of Mohammed Deif, a leading Hamas military commander.
While consensus exists regarding the certainty of an Iranian response, there is sharp debate within political and military circles over the nature of this retaliation. The targeted nature of the Israeli strikes suggests that a direct and immediate Iranian response may be needed to restore its deterrent credibility. However, Iran’s extensive network of regional proxies presents an alternative, allowing Tehran to retaliate indirectly while avoiding the military and economic costs of direct confrontation. This calculation has become more critical following the U.S.’s declaration that it would militarily defend Israel against any Iranian attack, reaffirming its earlier stance on Iranian missile strikes against Israel in April.
Predicting the nature of Iran’s response can be facilitated by examining the pattern of its previous reactions to similar attacks, particularly given Iran’s long history of confrontations following the 1979 revolution and its enduring hostility toward the U.S. Among these conflicts, the one most analogous to the current situation is the so-called Tanker War, which took place between Iran and Iraq from 1984 to 1988. Iran successfully drew the U.S. into a large-scale military engagement in the Arabian Gulf during this period. This scenario holds significant parallels to today’s tensions, as will be detailed later.
This paper, therefore, aims to analyse the similarities and differences between Iran’s current posture and its stance during the Tanker War from multiple perspectives—military, political, and economic—both internally externally. By comparing the dynamics at play, including the role of the U.S. in both scenarios, this analysis seeks to clarify what can be expected from Iran in light of these combined variables.
6 Aug 2024
Strategic Ramifications of Unrest in Bab El Mandab: The Arab Cost
The term “unification of arenas” emerged in the discourse of the Arab-Israeli conflict following the 2021 Sword of Jerusalem Battle. This military and ideological strategy is primarily linked to Iran’s regional proxies within the “axis of resistance.” This coalition includes Hezbollah, Hamas, the Houthis, and various Iranian-backed militias in Syria and Iraq. Its objective is to enhance operational coordination among these groups to counter Israel and diminish American influence in the region, aligning with Iranian strategic interests. The approach involves launching simultaneous actions across different fronts, including Lebanon, Gaza, and Yemen, to orchestrate a unified battle against common adversaries, particularly Israel and the United States (U.S.).
While this strategy had been employed on a limited scale prior to October 7, it achieved unprecedented levels of coordination following these operations. The execution involved dividing targets within Israel, with coordinated attacks from Gaza, Lebanon, Iraq, Syria, and Yemen. This meticulous synchronisation and sequence of missile and drone strikes overwhelmed Israeli air defences, with some attacks originating from Yemen and reaching targets in Tel Aviv.
These agents, particularly the Houthis, did not limit their actions to threatening Israeli facilities. Their strikes extended to disrupting navigation in the Bab El Mandab Strait off the Yemeni coast. The Houthis conducted numerous attacks on ships they claimed had ties to Israel, whether through state ownership, ownership by individuals with Israeli citizenship, or simply passing through Israeli ports. This broad targeting strategy encompassed a significant portion of the traffic in this crucial strait for global trade, particularly affecting Arab oil-exporting countries and Egypt, which relies heavily on the Suez Canal for its maritime traffic. As a result, shipping routes have shifted from the Suez Canal to the Cape of Good Hope, prompting long-term strategic transformations and immediate economic repercussions for the Arab countries involved. This analysis aims to assess the Bab El Mandab Strait's importance for Arab countries and explore the strategic implications of its disruption on their economies.
3 Jul 2024
Sacrifice Sustainability – Does it Impact Hajj Rituals?
Hajj, the fifth pillar of Islam, is a highly anticipated ritual for many Muslims. As the global Muslim population grows and financial conditions improve, the demand to perform Hajj has increased. However, pilgrims encounter numerous challenges, particularly regarding the ritual of sacrifice. After completing the stoning of the Jamarat, pilgrims perform the sacrifice—slaughtering a sheep, cow, or camel—as an act of devotion to Allah Almighty. This analysis seeks to explore the specific challenges associated with the sacrificial ritual.
To be considered valid, a sacrificial animal must meet several criteria. It must be livestock—camels, cows, sheep, or goats—and adhere to Islamic age requirements: at least six months old for camels, two years for cows, one year for sheep, and six months for goats. The animal must be free from defects, including lameness, blindness, illness, or severe emaciation. It must be slaughtered in designated holy locations and within the timeframe set by Islamic law, from after Eid al-Adha prayer until the final days of Tashreeq (the 11th, 12th and 13th of Dhul-Hijjah.)
25 Jun 2024
The Threat of Darkness: Can Hezbollah Disable Israel’s Electric Grid
On June 19 and 22, Hezbollah released two recordings showing high-resolution aerial images, catching Israeli security authorities and regional observers off guard. Apparently captured by a drone flying at medium to low altitudes, the footage highlighted security and strategic sites, including fuel storage facilities, thermal power stations predominantly located in Haifa, and the city's docks. This move underscored the potential reach of Hezbollah's missiles and drones to critical Israeli energy infrastructure.
The release triggered widespread speculation about Hezbollah’s missile capabilities, with analysts suggesting these missiles could directly strike the highlighted facilities. Such an attack could further destabilise Israel's economy, which is already experiencing significant challenges. The current economic situation is considered one of the worst in Israel's history, rivalled only by the first two decades after the state's founding and the Yom Kippur War.
On the other hand, many of these analyses have overlooked the Israeli electrical grid's distribution of generation stations, electrical load, maximum voltage, and generation sources, leaving the assessment incomplete. Even if Hezbollah’s missiles were to reach these stations and hit their targets with enough power and accuracy to disable them, it does not necessarily mean the entire electrical grid would be taken out of service or significantly reduce its capacity to produce electrical energy, which could impact daily life in Israel.
This analysis aims to review the generation stations, their capabilities, and their locations within Israel to investigate the potential impact of Hezbollah’s anticipated attacks on these facilities.
5 Jun 2024
Rescheduling: Prioritising Arms over Development on the European Parliament’s Agenda
European Parliament (EP) elections have historically garnered less interest from European voters,* as domestic issues have typically dominated their concerns. Consequently, topics such as defence and security have seldom been central to European election campaigns. However, this situation has changed dramatically in recent sessions. The influx of refugees arriving on European shores and the ominous threat of war looming over the continent have shifted the focus. As a result, Europe now finds itself precariously close to a crisis that threatens to undermine the development and reconstruction efforts of the past seventy years.
Therefore, regional issues began to be politicised and exploited in European Parliament elections as security and defence issues became more urgent. Parties shifted away from discussing the Union's broader policies, focusing instead on these pressing issues, which started to play a significant role in shaping voter preferences. Consequently, these topics became more influential in determining electoral outcomes at various local government levels, ultimately impacting decisions at the level of the European Union (EU).
This analysis examines the positions and attitudes of the main groups within the European Parliament on crucial defence issues facing the EU and how these positions are reflected in the political formulation of their policies.
17 Apr 2024
The Fallout of Escalating Iranian-Israeli Tensions
The Iranian Revolutionary Guard's Air Force made a historic move by launching a direct assault on Israel in an operation dubbed "The True Promise," marking the first instance of such an attack originating from Iranian territory. Late on Saturday, April 13, 2024, Israeli cities were subjected to a relentless barrage of drones and ballistic missiles, signalling a significant escalation in tensions between the two nations. This offensive action follows Iran's earlier pledge to retaliate against Israel for its targeting of the Iranian consulate in Damascus, an incident that resulted in the deaths of seven Revolutionary Guard members, including two high-ranking leaders, on April 1.
This calculated escalation underscores Iran's unwavering commitment to defending its sovereignty and national interests while bolstering regional security. The global spotlight now shifts to the scale, sophistication, and broader implications of Iran's strike against Israel.
The Iranian assault on Israeli soil marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing conflict between the two adversaries, thrusting their hostilities from the shadows into the open arena of direct confrontation.
Against this backdrop, the Israeli response hinges on several key factors. Firstly, the extent to which Iranian proxies, such as the Houthis and Hezbollah, may actively participate in the conflict will influence Israel's strategic calculus. Secondly, the response will be shaped by the presence or absence of casualties among Israeli forces, as well as the effectiveness of its defence systems, bolstered by support from the United States, in mitigating potential damage. Lastly, how Israel opts to retaliate will be of paramount importance in determining the trajectory of the conflict.
Consequently, this analysis aims to elucidate the attack's ramifications and its economic repercussions on the parties involved in the conflict.
2 Apr 2024
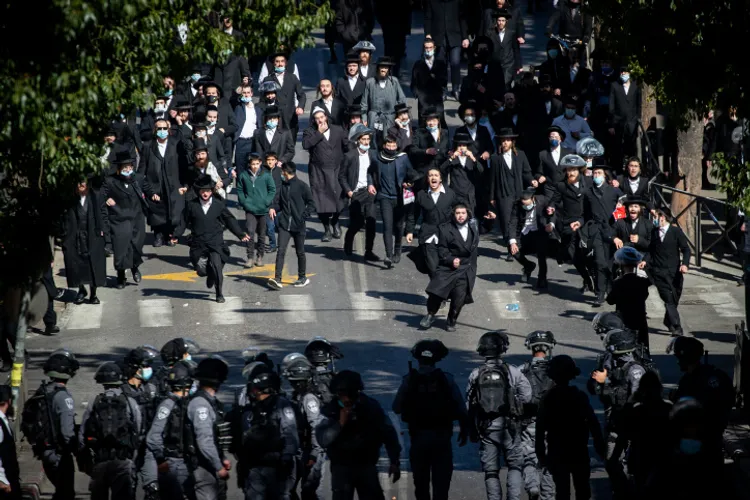
Israel-Hamas War: A Potential Breaking Point for Israeli Society
The dynamics between the Haredi Jewish community and the state of Israel are intricate and peculiar, shaped by many complex factors. Despite their historical opposition to the state's establishment and its Zionist underpinnings, they have emerged as prominent beneficiaries within Israeli society. Despite their active involvement in politics, with dedicated parties and ministerial representation in successive Israeli governments, the Haredi community seeks to diminish government authority over them. They maintain superficial compliance while preserving their self-organised societal structures.
These contradictions have been a continual source of critique within Israeli society since the State's inception. Successive Israeli administrations have consistently granted numerous privileges to the Haredi Jewish community, influenced by their political and religious sway. Chief among these privileges is their exemption from mandatory conscription, unlike other societal groups, accompanied by various financial incentives. However, the landscape is poised for significant transformation following the Gaza war.
This analysis aims to delve into the economic traits of the Haredi Jewish community and explore their broader economic impacts on Israeli society.
27 Mar 2024
The Power Orbit: The Space Internet Race and its Repercussions on Developing Nations’ Ability to Exploit Space
Globally, an estimated 4.2 billion people lack access to the internet, highlighting a major technological disparity. This digital divide disproportionately impacts rural and remote communities, hindering their access to essential healthcare, education, and economic opportunities. Traditional terrestrial infrastructure expansion often faces financial and geographical limitations in these regions. As satellite technology becomes increasingly accessible, space-based internet solutions emerge as a potential alternative.
However, the lowering cost of satellite production and launch, coupled with the availability of technological complexities of operating in low-earth orbit (LEO) create a competitive landscape. Developed nations and corporations are vying for dominance in LEO, raising concerns about the future accessibility of this technology for developing countries. This article investigates the challenges arising from this intensifying competition and its potential consequences for the digital inclusion of developing nations.
19 Feb 2024
Global Navigation Systems and Houthi Missiles
The Houthi militia targeted shipping traffic in Bab al-Mandeb Strait, aiming to exert pressure on Israel to lift the siege on the Gaza Strip. This resulted in the striking of dozens of ships as they traversed the strait in both directions.
Between November 19, 2023, and January 29, 2024, a total of thirty-five ships were targeted. The series of attacks commenced with the seizure of the vessel ‘Galaxy Leader’ and concluded with the naval missile strike on the ship " ‘Lewis B. Puller.’
6 Feb 2024
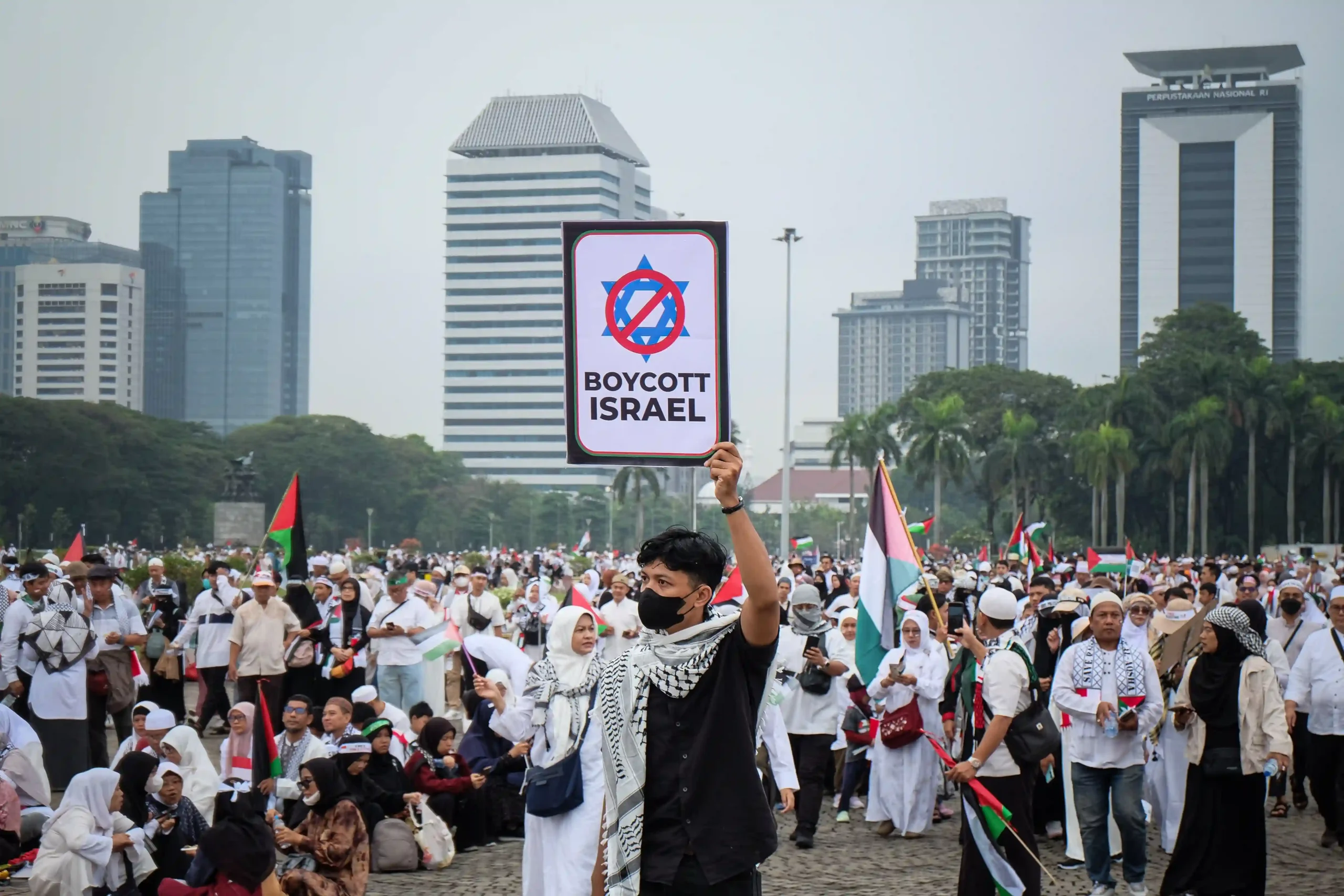
The Economic Impacts of Boycotts Against Israel and Supporting Companies
The documented history of employing a boycott as an economic weapon traces its origins to 432 B.C., Athens enacted the Megarian Decree, named after the city of Megara in ancient Greece. This decree comprised a series of economic sanctions, with a pivotal measure prohibiting Megarian goods from entering Athens. It extended to restricting Athenian ships from docking in Megara and, ultimately, barred Megarians from trading within the Athenian market.
In response, Megara and its allies in the Peloponnesian League took retaliatory economic actions, prominently featuring a boycott of Athenian goods. This reciprocal economic pressure adversely affected both entities, culminating in the onset of the Peloponnesian War. Lasting approximately 27 years, this conflict subsequently impeded the growth and continuity of Greek civilisation.
The following centuries witnessed the global utilisation of economic boycotts for various political purposes, primarily targeting the party subject to the sanctions, causing it to abandon a particular policy. Noteworthy instances include the Jews' first-century B.C. boycott of Roman goods, a protest against Roman occupation. In the 16th century, the Dutch Republic boycotted Spanish goods in opposition to Spanish rule. Additionally, during the 18th century, the U.S. colonies boycotted British goods as a protest against exorbitant taxes.
Contrary to common belief in the Arab world, the weaponisation of economic boycotts is not a recent phenomenon. Over the past two centuries, numerous academic studies have comprehensively examined and analysed its impact on both the boycotting and boycotted economies. These studies aim to gauge the effectiveness of economic boycotts in realising their intended goals.
The tactic of economic boycotts made its debut in the context of the Arab-Israeli conflict in 1922, when Palestinian Arab leaders initiated a boycott targeting Jewish-owned businesses in Palestine, aiming to inflict economic harm upon the Jewish population. These boycott attempts persisted sporadically throughout the 1930s and 1940s, with a notable instance occurring in 1936 when Palestinian Arab leaders advocated for a comprehensive boycott of all things associated with Jewish identity, even resorting to physical violence against Arabs who disregarded the boycott. Despite these efforts, the boycott proved unsuccessful, given the significant reliance of the Palestinian population on Jewish professionals such as lawyers, doctors, and hospitals.
Subsequently, the boycott assumed a regional dimension in December 1945 when the six states comprising the Arab League jointly issued the initial call for an economic boycott against the Jewish community in Palestine. This declaration went beyond mere encouragement and urged all Arab countries, regardless of their League membership status, to prohibit the trade of Jewish products.
In 1946, the situation evolved with the Arab League establishing the Permanent Boycott Committee, intending to heighten the implementation of the boycott. Despite these efforts, the boycott's lack of success became evident, as outlined in the first annual report of the Boycott Committee.
Following the committee's shortcomings, the League swiftly bolstered its structure, transforming it into the Central Boycott Office. Headquartered in Damascus, it established branch offices in every member state of the Arab League. The pivotal role of the county commissioner was instituted to lead the office, accompanied by appointed deputies serving as liaison officers accredited by each member state of the Arab League.
The Central Office in Damascus assumed the pivotal role of coordinating the boycott in tandem with its affiliated offices. It was responsible for presenting regular reports to the Council of the Arab League. Starting from 1951, semiannual meetings were scheduled to synchronise boycott policies and formulate blacklists of individuals and companies breaching the boycott. The punitive measures were executed locally, with each member state implementing decisions through legal and administrative executive procedures.
From 1951 to the present moment of composing this analysis, calls for boycotts have been recurrent with each political conflict between Palestinians and Israelis. They have been wielded as a means of resistance against Israeli occupation and its perceived unjust policies toward the Palestinian population. However, these calls have generally manifested in three distinct patterns, as explained below.
30 Jan 2024
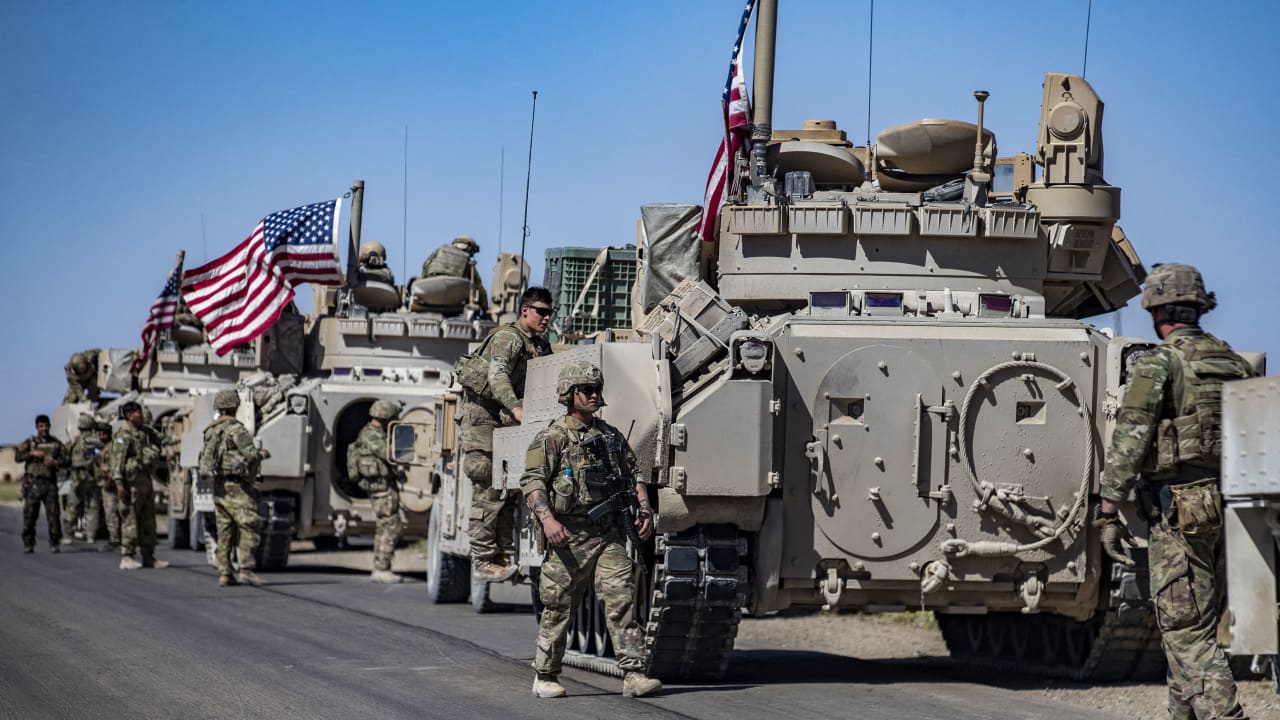
The Vicious Cycle of Violence: Next Steps Post-Jordan Attack
On Jan. 28, 2024, a significant drone strike occurred at an American military outpost situated along the Jordanian-Syrian border. The targeted attack led to the death of three American troops, with 34 additional personnel sustaining injuries, as reported in the latest statement released on Jan. 30, 2024.
This event holds profound implications and is poised to instigate repercussions that warrant careful analysis and monitoring. Notably, it marks the first instance of American service members being killed by hostile fire in the Middle East since the commencement of the Israel-Hamas War. The attack's location and timing carry additional connotations, underscoring the need to anticipate and evaluate the potential developments that may occur.
Moreover, the Islamic Resistance in Iraq (IRI) claimed responsibility for the attack in a statement, explicitly stating, “We targeted four enemy bases, including three situated in Syria: Al-Shaddadi base, Al-Rukban base, and Al-Tanf base (located near the Syrian-Jordanian border). The fourth targeted base is within the occupied Palestinian territories, identified as the Zevulun Naval Facility.”
8 May 2023
Drums of War: Clean Energy Conflict on Both Sides of the Atlantic
The relationship between the United States and the European Union serves as a model for economic integration and collaboration in trade and investment between two non-regional parties. Both sides are considered each other's significant general trading partners when it comes to commercial relations for goods and services. Conversely, China surpassed the United States as Europe's top trading partner for goods in 2020. In 2022, trade in goods between the two sides exceeded $900 billion, while trade in services exceeded $500 billion.
Despite its strength, this relationship has its share of trade disputes, primarily fuelled by the growth of bilateral trade and each side's desire to further enhance its surpluses by entering the other's market. These disputes sometimes even reached the World Trade Organisation (WTO), most recently in 2018 when the US imposed 25% and 10% tariffs on imports of steel and aluminium from the EU based on national security grounds, to which the EU replied in kind.
However, the nearly 17-year-old dispute for control of the world's civil aviation industry between the two giant companies, American Boeing and European Airbus, was the most intense ever. Each side, "the United States and the European Union," made an effort to provide government aid to its company against the other. As the dispute escalated, both sides imposed retaliatory tariffs on a portion of each other's imports, which by 2021 totalled $11.5 billion. Eventually, in light of their disagreement with China, the two sides agreed to a trade truce, which stopped the dispute.
With every dispute between the two sides, the world hangs its breath due to their significant impact on the international economy, the shift forced by such a conflict in supply chains and the potential global slowdown. The world has been concerned about a similar situation since US President Joe Biden successfully passed his Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 in August 2022, which heralded the beginning of a prolonged war on both sides of the Atlantic in a world already dominated by trade and military conflicts between the East and the West.
This article analyses the American Inflation Reduction Act and predicts how this Act will impact the global economy in light of the current unstable economic situation.
2 Apr 2023
Restoring Balance: Impacts of Automation on UAE Labour Force
According to the McKinsey Global Institute report between 400 million and 800 million people worldwide could be displaced by automation and need to find new occupations by 2030, with 75 million to 375 million of those affected need to move to another new jobs and learn new skills.
Over the last two decades, there has been a surge in interest in automation and digital technologies, as well as their implications for our societies. Several writers have calculated experimentally the impact of automation technologies on employment and people by examining technology adoption at the business or industry level in previous years and related this to labour market outcomes, but their conclusions have been mixed. Some studies find that automation technologies positively impact employment, while others show that they have a negative impact.
Our study examined the impact of automation on UAE in terms of demographics, employment and economic sectors by implementing several scenarios of automation. These scenarios revealed that, in most cases, automation will positively impact UAE in terms of some macroeconomic indicators, and will lead to its economic growth and stability. Finally, we provided some recommendations that will enhance and facilitate the transition to automation in the UAE.
15 Mar 2023
BRICS’ Future Currency and the Global Financial System
Alexander Babakov, vice-president of the State Duma, stated on Thursday, March 6th, that the BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) alliance is working on creating its own currency and will submit proposals at the organisation's upcoming summit in August in South Africa.
The declaration was not only the culmination of cooperation efforts between the fifth emerging economies to preserve their position in the global system after Western powers worked since the 1990s to prevent them from assuming their positions in international economic organisations — especially the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund. However, it also raised many questions about the impact of the new currency on the global financial system, particularly given the strength of the five economies in the international arena and the alliance's stated intention to expand to include additional developing nations such as Saudi Arabia, Iran, Egypt, and Bangladesh.
This paper tries to predict the consequences of creating the new currency on the structure of the global financial system and its impact on other major currencies, considering the European Union's experience in creating the Euro.
2 Mar 2023
In the Eye of the Storm: Food Security in MENA Region
According to a report by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) on the state of food security and nutrition in the world in 2022, it is estimated that between 702 and 828 million people were affected by hunger in 2021, consisting of 278 million people in Africa, 425 million in Asia, and 56.5 million in Latin America and the Caribbean. The number has grown by about 150 million since the outbreak of Covid-19. The Russia-Ukraine War, involving two of the biggest producers in agriculture and staple cereals globally, is disrupting supply chains and further affecting global grain, fertilizer, and energy prices, leading to shortages and fuelling even higher food price inflation. Additionally, food security is a significant challenge in the Arab region, which is facing rising economic, socio-political, and environmental challenges impacting the food security of its growing population.
Hence, our study has examined the factors that affect food security, and our analysis allowed us to determine the top five factors affecting food security: climate change, conflict, overpopulation, inflation, and scarce resources. The study will analyze each factor separately and their effect on food security globally and in many regions, with a focus on the Arab region. Secondly, the study will analyze factors of food insecurity separately and its impact on four significant countries: Egypt, the United Arab Emirates, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, and Jordan.
We found that the factors we examined have mainly negative effects on food security, with the exception of climate change, which will positively affect some regions for the time being, and natural resources, which has some aspects that effect food security positively. Additionally, we found that the factors are interconnected since for example, conflict negatively affects food security, and it could increase food prices, as in the current Russia-Ukraine War. Likewise, the adverse impacts of climate change are expected to raise food prices further and dampen the region’s food demand translating into direct increases in malnutrition levels.
Finally, after reviewing the effects of factors on food security, we elaborated some recommendations in order to deal with the adverse effects.
25 Feb 2023
Radical Transformations: Repercussions of Russian Oil Price Cap on Global Energy Trade Paths
In February 2023, the European Union (EU) agreed to set a price cap on Russian refined oil products at $100 per barrel. The EU also set the price cap on Russian crude oil at $45 after setting it at $60 per barrel in cooperation with the Group of Seven (G7) countries in early December 2022, according to a periodic review every two months.
The European decision aims to control energy prices generally and stop price fluctuations that have affected global markets since the Covid-19 pandemic and the following events, particularly the commodity supercycle and the Russian-Ukrainian war. Furthermore, the Europeans aim to cut off the funding sources from the Russian federal budget that funds the military operation in Ukraine. In 2021, Russia exported oil worth around $212.4 billion of its $492.3 billion total exports to the rest of the world.
In response, the Russian government issued a decree on December 28, 2022, prohibiting the export of crude oil and petroleum products to countries with imposed price caps. Europe is the third-largest oil importer in the world after China and the United States. Conversely, Russia ranks first on the list of suppliers to the European continent while ranking second worldwide regarding oil exports. Therefore, we track in this article how the price cap decision may alter the global energy transmission paths.
20 Feb 2023
Return of Protectionism: The US War on Globalization
Following the First and Second World Wars, the world order was founded on open international trade to ensure peace and security. Where the major powers realized that the two world wars occurred as a result of international competition over resources and markets, and therefore the Bretton Woods system came intending to establish a stable international monetary system that encourages global economic cooperation. Its main objective is to avoid the destabilising effects and competitive devaluations of currencies that were used in the period between and before the two world wars, to provide a framework for the free international exchange of goods and services, and to promote economic growth and stability in the long term.
14 Feb 2023
New Gulf: Russo-Ukrainian War and Emergence of North Africa’s Energy Sector
The Russian-Ukrainian war created significant uncertainty in the world’s energy markets and disrupted trade relations between the second-largest energy exporter and the second-largest energy importer. This disruption strongly signals a shift in the global energy supply chains, as indicated in a previous analysis. In the short term, Europe is expected to turn to the Arab Gulf to fill the gap left by the lack of Russian energy products.
However, in the long term, Europe will need to find sources that are highly sustainable, affordable, and less harmful to the environment than oil. This is because petroleum usage is incompatible with the European Green Deal (EGD), which aims to achieve carbon neutrality for the entire European continent by 2050. Furthermore, the EGD seeks to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the mainland by around 55% below 1990 levels by 2030, which is unattainable with continued oil usage.
As a result, Europe will turn to its neighbours, particularly those in North Africa, who possess a variety of energy sources that can help it achieves its objectives and guarantee energy sustainability. Thus, this article explores Europe’s energy requirements and assesses the potential of North Africa’s energy resources to meet these requirements.