14 Oct 2025
Not All Quiet on the Western Front: Europe’s Next War
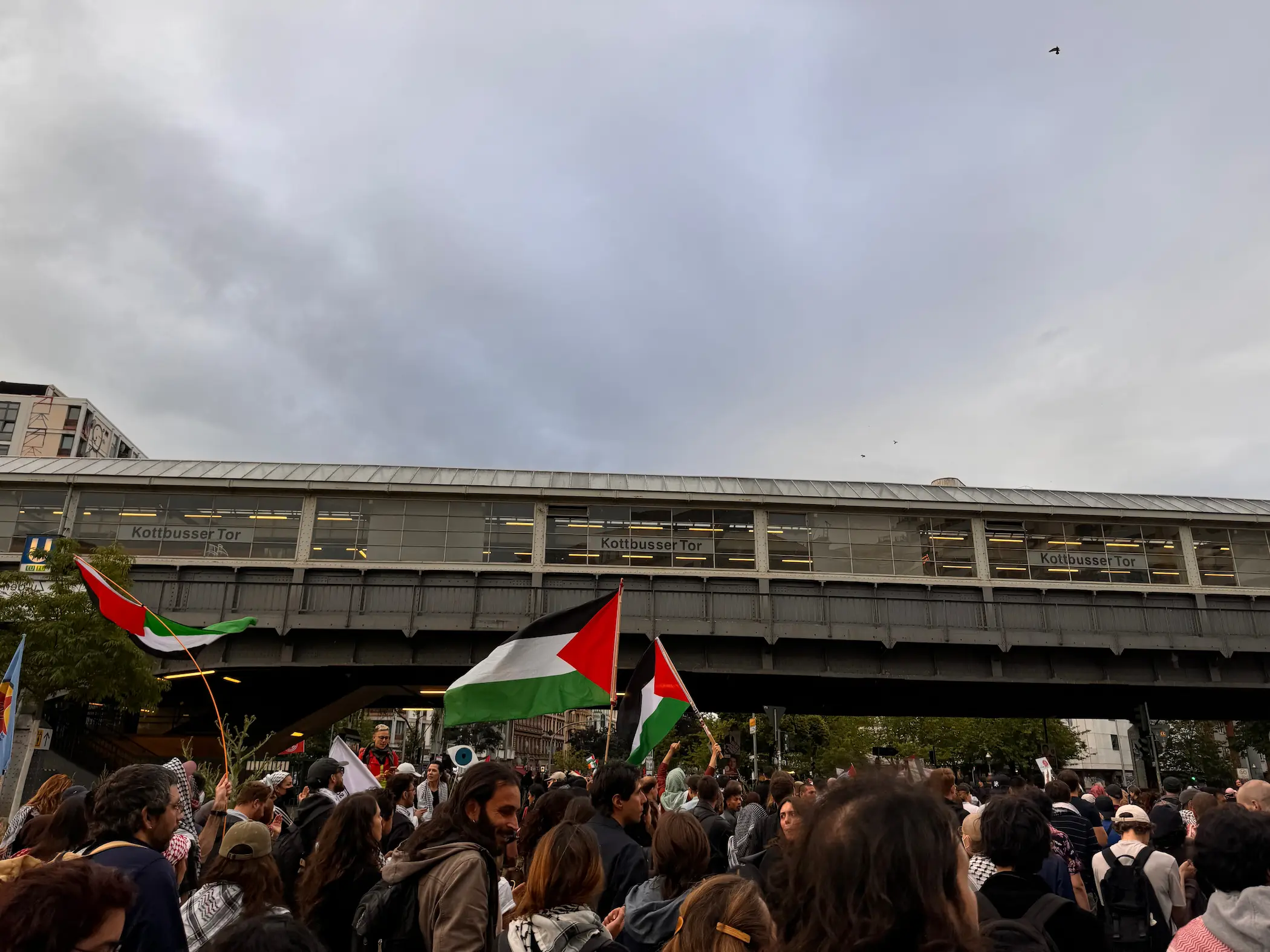
“Poland is at its closest to open conflict since World War Two,” warned Prime Minister Donald Tusk, after a sudden Russian airspace violation rattled the country. On September 9, a swarm of Russian drones entered Polish skies, prompting NATO aircraft to scramble and intercept several of them. It marked the first direct encounter between NATO and Moscow since Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022. While the incident might have been a test by Putin to gauge NATO’s and Europe’s response, it also raises the specter of a potential war between Poland and Russia. Given Poland’s critical role within NATO and the EU, far greater than Ukraine’s, the implications of such a conflict would place the entire continent in Jeopardy. The pressing question now is: how likely is this war to erupt, and would Europeans bear the brunt?
9 Oct 2025
US Intelligence Support Signals a New Phase in the Russia-Ukraine War
On October 1, U.S. reports stated that President Donald Trump gave the green light to provide Ukraine with intelligence information to strike deep into Russia’s energy infrastructure sites, while studying providing Kyiv with long-range weapons that can be used in such strikes. The reports also indicated that Washington is encouraging the NATO allies to take similar actions.
The U.S. has already been providing intelligence to Ukraine since the beginning of the war; however, Trump's signalling to provide more sensitive information could hold different consequences on the outcomes of the war. Since his second-term inauguration, Trump has vowed to end the Russia-Ukraine war, so does this decision come in parallel to the American President's ambition to broker a peace deal between Moscow and Kyiv, and how this might implicate the Russian and Ukrainian sides.
1 Oct 2025
Who Stands to Gain from the H-1B Visa Shake-Up?
Since taking office, U.S. President Donald Trump’s unpredictable decisions have become a puzzle to follow, let alone to anticipate. Amid this growing political turbulence, a dose of rational analysis is badly needed. His recent move on the H-1B visa program, for instance, has reverberated across the globe. Though seemingly aimed at harrassing India, the policy has instead cornered the United States itself, fueling economic strain, draining valuable talent, and unsettling the tech industry. The ripple effects are already visible in Silicon Valley and among those aspiring to join it. Yet, this turbulence also opens a window of opportunity. Nations in Europe, Asia, and the Gulf, if swift and strategic, could position themselves to attract the very talent cast aside by Washington. Still, seizing this chance is no straightforward task. It demands structural reforms, long-term vision, and proactive policies. Dislodging Silicon Valley from its pedestal is not impossible, but neither is it simple or automatic. What matters now is understanding the impact on the U.S., its economy, its talent pool, and recognizing what ambitious countries must do if they wish to challenge the world’s current tech giant.
30 Sep 2025
An Unequal Cost: How Space Debris Deepens the Exclusion of Developing Nations from the Economies of the Future
Since the launch of the first satellite in 1957, the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) has undergone a profound transformation from a near-empty frontier into a congested and polluted environment shaped by decades of human activity. Non-functional satellites, spent rocket stages, and fragmentation debris from collisions and explosions have accumulated to a mass exceeding 14,700 tons. Critical events have amplified the scale of the problem, most notably China’s Anti-Satellite Test (ASAT) in 2007 and the 2009 collision between the U.S. Iridium-33 and Russia’s Kosmos-2251, which together generated nearly one-third of all catalogued debris in LEO.
This material is unevenly distributed but highly concentrated between 750 and 1,000 kilometres, an orbital belt central to Earth Observation and communications. Objects in this altitude range can persist for centuries, while in the Geostationary Orbit (GEO) debris may remain indefinitely, underscoring the long-term persistence of the hazard. Consequently, orbital space has shifted from an open frontier to a finite and polluted resource requiring collective governance.
This study examines the economic and political dimensions of space debris. It assesses the direct costs borne by operators, the cascading risks to terrestrial infrastructure such as Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) and weather forecasting, and the disproportionate challenges facing developing nations. It concludes by analysing potential responses, ranging from mitigation strategies to Active Debris Removal (ADR), within the broader framework of international governance and global equity.
26 Sep 2025
The Global Economic Impacts of Starlink Outages: From Operational Fragility to Pathways of Resilience
In recent years, Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations have emerged as a transformative layer within the global digital infrastructure, marking a departure from their original role as connectivity solutions for remote regions. These systems are now embedded within the operational cores of critical sectors such as civil aviation, maritime logistics, financial markets, and defence. The clearest manifestation of this structural shift is Starlink, operated by SpaceX, which by mid-2025 had exceeded 7 million users across more than 150 countries, with exponential growth rates in high-value, latency-sensitive industries.
This rapid technological and geographical expansion has positioned Starlink as a globally integrated utility—yet one that operates outside conventional regulatory regimes. It represents a structural concentration of control over global data flows in a single, privately held entity. The dual outages that occurred in July and September 2025 exposed deep systemic vulnerabilities within the Starlink network, including software architecture fragilities and environmental sensitivities to space weather events. These incidents prompted urgent questions about the stability of a critical infrastructure layer that now underpins sectors central to national sovereignty and global economic coordination.
This report interrogates the systemic risks embedded in the global economy’s growing dependence on LEO constellations through two interlinked analytical lenses. The first is a technical-political economy perspective, which examines the underlying architecture of the Starlink network and the typology of its failure modes—both endogenous and exogenous. The second is a forward-looking, scenario-based assessment that models the potential global economic consequences of a 24-hour Starlink outage in 2032. Through this dual approach, the analysis traces the contours of a new strategic dilemma: how to govern an emergent, transnational infrastructure whose failure could trigger multi-sectoral crises at planetary scale, yet whose design and control remain entirely privatized.
18 Sep 2025
The Semiconductor Cold War: U.S. vs. Russia, China and India
The global competition over semiconductors and related military technologies has become the central axis of great-power rivalry. The United States maintains its leadership in the global semiconductor industry, with American companies securing roughly half of the global semiconductor market. However, this dominance faces a growing challenge from China, which accounted for 20% of global semiconductor sales in 2024. Beijing’s ambition to achieve self-sufficiency in semiconductors is steadily advancing despite ongoing trade tensions and intellectual property restrictions imposed by Washington amidst the broader ‘tech war.’ China aims to reach 50% self-sufficiency in semiconductor production by the end of the year, reinforced by significant investments in R&D and market expansion by Chinese firms.
In contrast, Russia’s position in semiconductor-dependent military industries is increasingly constrained. Although Russia retains expertise in weapons design, its reliance on imported materials and advanced chip-making equipment from Western countries exposes critical vulnerabilities. Western sanctions, introduced in response to Russia’s military actions in Ukraine, have sharply limited Moscow’s access to these essential inputs. In response, Russia has sought alternative suppliers, with China emerging as its largest source of semiconductor materials. These dynamic forms part of the broader Russia-India-China (RIC) trilateral framework, underpinning Moscow’s strategic pivot toward Eastern partnerships.
Meanwhile, India is rapidly evolving as a significant player in the semiconductor sector. The country’s announcement in September of its first indigenous chip, “Vikram 32,” marks a milestone in New Delhi’s pursuit of technological self-reliance and signals India’s potential emergence as a competitor to U.S. semiconductor dominance. India’s increasing engagement with Russia and China reflects a pragmatic alignment based on mutual interests, particularly in the context of escalating policy tensions with Washington. Notably, U.S. tariffs imposed on India’s trade in Russian oil have further incentivized this trilateral collaboration.
Collectively, the China-Russia-India “troika” represents a coalition of shared interests rather than a formal ideological alliance. Should this partnership strengthen, it could significantly bolster their semiconductor manufacturing capabilities and pose a formidable challenge to the American industry. Nevertheless, lingering frictions—such as unresolved border disputes, differing economic priorities, technological gaps, and the impact of sanctions—are likely to impede seamless technological integration. The United States still wields substantial influence over India, with opportunities to attract New Delhi through increased investments, tariff reductions, and advanced technology cooperation. Ultimately, the trajectory of the RIC semiconductor partnership holds profound implications for the global order. A successful integration of this “troika” chip industry with their respective military technologies could catalyse the rise of a multipolar system, revolutionizing surveillance, air defence, drone capabilities, and the broader defence industrial base, thereby reshaping international power dynamics.
18 Sep 2025
An Isolated Israel
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu recently acknowledged that Israel is entering a phase of economic and political isolation internationally, largely due to its ongoing military actions in Gaza. He warned that this isolation may last for years and insisted that Israel must adapt by becoming more self-sufficient, especially in its weapons manufacturing capabilities. Netanyahu described this shift as moving toward an economy with "autarkic characteristics," a term he said he despises since he has long supported free-market policies. Nonetheless, given potential export bans and economic sanctions, he emphasized Israel's need to be both "Athens and super-Sparta," implying a combination of intellectual and military self-reliance to withstand these challenges.
His comments are a rare admission that Israel faces significant global backlash and diplomatic estrangement due to the nearly two-year war in Gaza. Several Western countries, such as Spain, have cancelled arms deals with Israel over the war, with a U.N. Independent International Commission finding that Israel is committing genocide, and a slew of other countries have officially recognized a Palestinian State.
Netanyahu's remarks mark a rare acknowledgment of the changing international environment around Israel. This mounting isolation not only underscores Israel’s diplomatic challenges but also highlights the growing vulnerabilities within its economy, as sanctions, boycotts, and the loss of arms contracts emerge as direct consequences of its genocide in Gaza.
17 Sep 2025
The GPS Battlefield: The Invisible War in the Middle East
Wars are no longer confined to missiles, drones, or soldiers on the battlefield; increasingly decisive struggles are taking place in the invisible realm of signals that quietly guide planes through the sky, ships across narrow straits, and even the timing of financial markets. At the heart of this new contest lies the Global Positioning System (GPS), once praised as a scientific triumph and gifted to the world as a free public good, increasingly repurposed into a weapon that is inexpensive to disrupt, difficult to trace, and capable of inflicting consequences far beyond the battlefield.
The recent jamming of European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen’s aircraft served as a stark reminder that even the highest levels of leadership are not immune, but what may appear to be isolated incidents in Europe are in fact part of a broader pattern that has taken deep root in the Middle East. In a region where the world’s most critical energy chokepoints converge, navigation interference is no longer a rare abnormality but an increasingly routine feature of conflict, carrying implications that stretch from military readiness to economic stability and, ultimately, to the daily lives of millions.
15 Sep 2025
Trump Peace Play: Three Futures for Russia-Ukraine War
Amid Trump’s meetings with Russian & Ukrainian counterparts to reach a prolonged ceasefire, questions arise about the possibility of a successful peace plan occurring between Moscow & Kyiv with a U.S. mediation. Yet, with Putin’s demands from one side and Trump’s ambiguous promises to Zelensky from the other side, will the Ukraine war come to an end?
17 Aug 2025
Domino Effect: Are More States Moving Toward Recognising Palestine?
Recent statements by France, the United Kingdom, and Canada—subsequently echoed by other European states—on their intention to recognise a Palestinian state in September mark a notable transformation in the policies of major Western powers toward the Palestinian question. This development comes against the backdrop of the deepening humanitarian catastrophe in Gaza, manifested in widespread famine and a death toll exceeding 60,000, which has further amplified international calls for an urgent political resolution to the decades-long Israeli–Palestinian conflict.
The announcements from Paris, London, and Ottawa—particularly France’s unconditional pledge alongside the conditional approaches adopted by the United Kingdom (UK) and Canada—represent a clear departure from traditional diplomatic norms, which had long tied recognition of a Palestinian state to the conclusion of a comprehensive negotiated peace agreement. This shift reflects mounting frustration over the stalled peace process, coupled with a growing conviction that conventional pathways have ceased to yield results. Recognition of Palestine is now increasingly seen not merely as the outcome of peace but as an instrument to catalyse the political process, thereby reshaping the diplomatic tools available for addressing the conflict and establishing a precedent that other states may exploit to strengthen international pressure.
At the international level, between 140 and 147 of the 193 UN member states already recognise Palestine as a sovereign state. This broad consensus provides the reference framework for understanding the recent decisions taken by France, the UK, and Canada. Notably, these three countries are all members of the G7, none of which had taken such a step before France’s declaration. France—Europe’s most populous nation—thus emerges as a prominent actor in this diplomatic shift, with both France and Canada poised to become the first G7 states to extend formal recognition to Palestine.
By contrast, the U.S. remains the sole permanent member of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) that has yet to recognise the State of Palestine. This imbues the current shift with symbolic weight, laying the groundwork for a recalibration of diplomatic pressure on both Israel and the U.S., and potentially encouraging other hesitant Western states to follow suit. The divergence of positions within the Atlantic powers also underscores how internal pressures and the urgency of the humanitarian crisis have shaped the emergence of more assertive stances. Against this backdrop, this analysis explores the drivers behind this shift and its political and security implications for the states concerned, alongside the anticipated responses from Israel and the U.S.
11 Aug 2025
Middle East in Energy Transition: From Stopgap to Global Architect
On July 28, 2025, during a joint press conference in Scotland with British Prime Minister Keir Starmer, U.S. President Donald Trump issued an unexpected ultimatum to Russia. He declared that the Kremlin had no more than 10 to 12 days (until approximately Aug. 8, 2025) to make tangible progress toward ending the war in Ukraine. Should Moscow fail to comply, Trump warned that President Vladimir Putin would face a sweeping package of economic sanctions and severe trade restrictions. This escalation came on the heels of prolonged diplomatic stagnation and Trump’s increasingly vocal frustration with Russia’s continued military operations.
Subsequently, on July 31, 2025, former Russian President and current Deputy Chairman of the Russian Security Council Dmitry Medvedev responded with a pointed and ominous message via his Telegram channel. In his remarks, he invoked the “Dead Hand”—Russia’s semi-automated nuclear retaliation system designed to launch a retaliatory strike even in the event of a complete decapitation of the nation’s leadership.
In response, President Trump ordered the deployment of two U.S. nuclear submarines to strategic positions, framing the move as a necessary precaution in the face of what he described as “extraordinarily dangerous” nuclear threats. Notably, he refrained from specifying whether the submarines were nuclear-powered only or also nuclear-armed—introducing deliberate strategic ambiguity and reinforcing the doctrine of pre-emptive deterrence through calibrated uncertainty.
What renders this sequence of events particularly significant is that the confrontation did not remain confined to the U.S. and Russia. Its repercussions quickly extended to India, which was thrust into the geopolitical crossfire. On July 31, the Trump administration announced the imposition of a 25% tariff on all Indian exports to the United States, accompanied by threats of further penalties targeting Indian firms that continue to purchase Russian crude oil or engage in defence cooperation with Moscow. The rationale behind this punitive action lies in New Delhi’s deepening energy relationship with Russia.
Although the Indian government has not officially announced any suspension of contracts with Russian suppliers, discreet directives were reportedly issued to state-owned refiners instructing them to explore alternative sources in the global spot market. This pivot has begun to materialize reflecting New Delhi’s attempt to maintain equilibrium between preserving its strategic autonomy and mitigating mounting U.S. pressure.
Yet the broader implications of this crisis extend well beyond geopolitical brinkmanship. What is unfolding is a systemic shock to the global order—one that is reverberating through energy markets, food security systems, arms trade corridors, and supply chains. The consequences will not be distributed evenly: while some Middle Eastern states stand to benefit from surging demand and price shifts, others may face acute vulnerabilities due to trade disruptions, inflationary pressures, or capital flight.
30 Jul 2025
What If: The Middle East Burns Next?
In 2023 a sobering milestone was met, the highest number of wildfires in the European Union (EU) since tracking began in 2000 by the European Forest Fire Information System. More than 500,000 hectares of land were burned, an area equivalent to half the size of Cyprus. The situation worsened in 2024, with wildfire-related fatalities rising sharply to 437, compared to 263 deaths in 2023.
Research consistently points to climate change as a primary driver behind this growing crisis. Not only is it increasing the scale of land burned, but it's also intensifying individual fires, extending fire seasons beyond the traditional summer months, and triggering blazes in regions previously untouched by such disasters. As this escalating threat edges closer to the Middle East, the pressing question remains: will the region be prepared, or caught dangerously off guard?